What are PCBs?
PCBs or Printed Circuit Boards have become thoroughly ubiquitous in today’s world. Before PCBs, all components were connected by mainly using wires. A PCB is a plastic board strengthen with glass, with Copper traces and pads covering it which connect together. These copper traces allow current to flow through the PCB, providing power to the different components that are situated on the board. This article will serve as a complete guide towards PCB basics and will also help you understand what PCBs are all about.
Understanding PCB basics begin by understanding the nature & applications of PCB itself. PCBs serve in many electronic devices like; TV, Mobile, Digital cameras. Computers parts like; Graphics cards, Motherboard, etc. It also functions in fields like; medical devices, industrial machinery, automotive industries, lighting, etc.
JLCPCB is the foremost PCB prototype & manufacturing company in china, providing us with the best service we have ever experienced regarding (Quality, Price Service & Time).
Classification Of PCBs
Starting our guide on PCB basics, we will first look at the classification of PCBs. PCBs can be classified on the basis of:
- Mounting Technology
- No. of Layers
- Flexibility
1) Classification on the Basis of Mounting Technology
Through-hole PCB
In a through-hole PCB, components are placed on the board by drilling holes through the PCB board & mounting the part, with solder pads on the opposite end. This method is easy to implement in single layer PCB but gets far too complex for Multi-layer PCBs where drilling holes through the PCB is more difficult & expensive.
Surface Mount PCB
In this type of PCB, components are small in size because these components have very small lead or no leads are required for mounting on the board. Here, in this technology, SMD components mount directly on the surface of the board, with no need to drill holes on the PCB.
2) Classification on the Basis of Number of Layers
Single Layer PCB
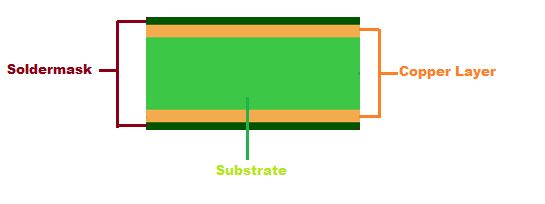
Single layer PCB is the most simple & commonly used PCB in today’s design market. As the name suggests, this type has only one layer of a conductive material such as a copper sheet. A solder mask then protects the copper sheet along with a silkscreen to mark all the components. One can easily identify a single layer PCB, as it has markings and traces only on one side.

Double Layer PCB
Double layer PCB consists of two layers of conductive material. in this type of PCB, a thin layer of conducting material, like copper is on both top and bottom sides of the board. In this kind of PCB, usage of vias is very common, which are two pads in corresponding position on different layers of the PCB board through an electronic connection by a hole through the board.
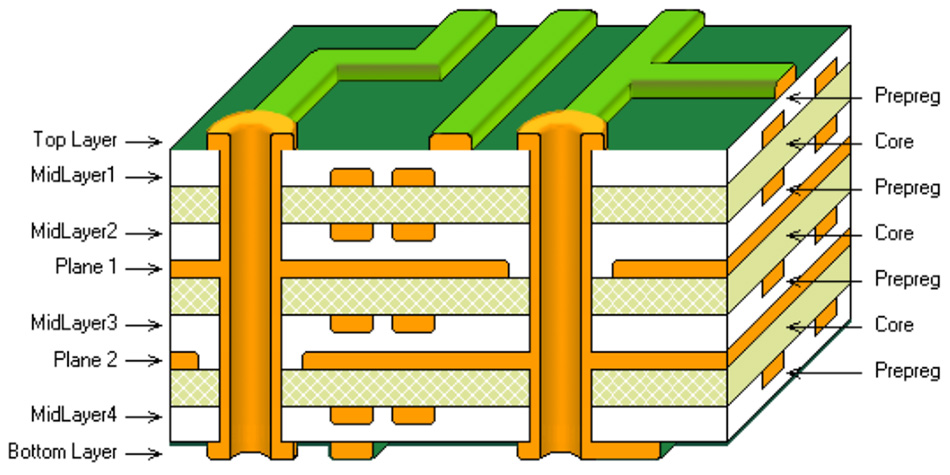
Multi-layer PCB
A Multi-layer PCB has at least 3 conductive layers of copper. It can be considered as batches of double-layer PCBs where the 2 conductive foils are glued and laminated with a dielectric sheet placed in between them. The manufacturing of Multi-layer PCBs is pretty complex since as the no. of layers increases, the thickness of copper sheets needs to remain in check so that the overall circuit board does not look too bulky.
3) Classification on the Basis of Flexibility
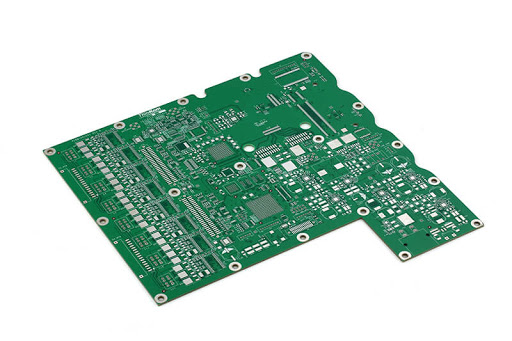
Rigid PCB
In Rigid PCBs, solid materials restrict the twisting of the PCB. Rigid PCB have different layer configuration like single layer, double layer and multi-layer Rigid PCB. Shape of this PCB does not change after installation. It functions as the base component for devices such as RAMs, CPUs & GPUs, since its average lifespan is very high.
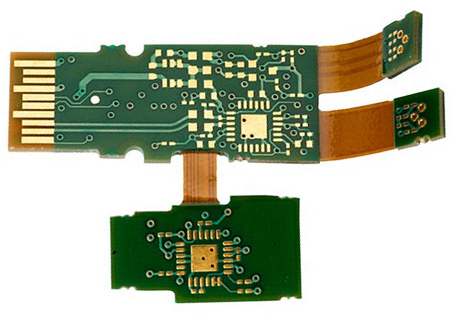
Flex PCB
Flex PCBs, get their name for their flexible nature of enabling any circuitry to fit any electronic device or a product, as opposed to building a separate housing to conform to the circuit board. This type of PCB uses flexible plastic material like polyimide, PEEK (Polyether ether ketone), or transparent conductive polyester film. It saves space and is also very light in weight. Flex PCB serves in applications such as LEDs, LCDs, flex solar cells, automotive industries, smartphones, cameras. Just like the Rigid PCB, it is also available for a single layer, double layer, and multi-layer PCB boards.
Flex-Rigid PCB
Containing a combination of both flexible & rigid PCBs, the Flex-rigid PCB boards consist of multiple layers of flexible PCB attached to a number of rigid PCB layer. They are ideal for their use in medical electronics, in devices such as pacemakers, pulse oximeter, etc.
In Conclusion, this guide is a comprehensive approach to PCB basics for beginners to electronics.