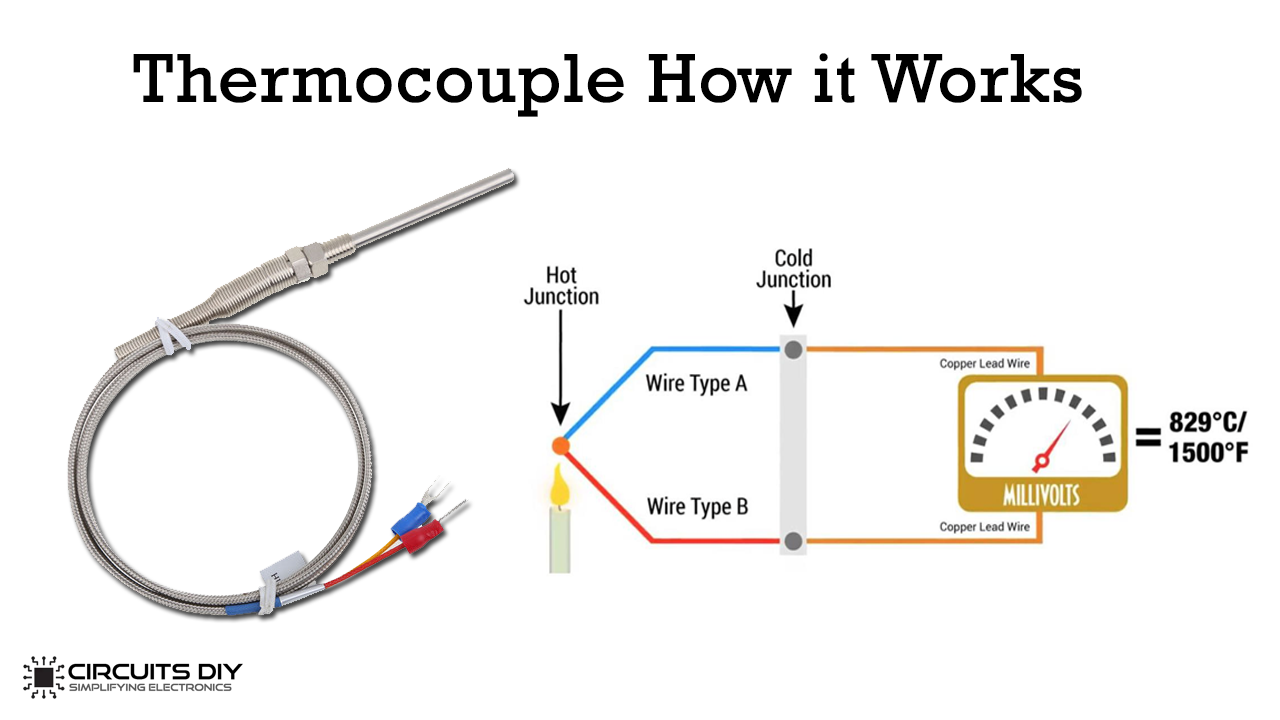
A Thermocouple is a type of temperature sensor which is used to measure temperature. It consists of two different types of metals that are joined together to form two junctions. One junction is connected to the body whose temperature is to be measured. The other junction is connected to a body of known temperature which is at a lower temperature.
The temperature difference causes the development of a voltage that is approximately proportional to the difference between the temperatures of the two junctions. The voltage can then be interpreted using thermocouple reference tables to calculate the temperature, or the measuring instrument can be calibrated to read temperature directly.

Working Principle
The thermocouple working principle mainly depends on the three effects namely Seebeck, Peltier and Thompson.
- Seebeck effect
When two different metals are joined together at two junctions, an electromotive force (emf) is generated at the two junctions. The amount of emf generated depends on the combinations of the metals.
- Peltier effect
When two, unlike metals are joined together to form two junctions, emf is generated within the circuit due to the different temperatures of the two junctions of the circuit.
- Thomson effect
When two, dissimilar metals, are joined together, the potential exists within the circuit due to temperature gradient along the entire length of the conductors within the circuit.
Types of Thermocouple
Thermocouples are available in different combinations of calibrations. The four most common types of calibrations are J, K, T, and E. Each calibration has a different temperature environment and range. Although the maximum temperature depends upon the diameter of the wire used in the thermocouple.
| Calibration | Temperature Range |
| J | 0° to 750°C (32° to 1382°F) |
| K | -200° to 1250°C (-328° to 2282°F) |
| E | -200° to 900°C (-328° to 1652°F) |
| T | -250° to 350°C (-418° to 662°F) |
Advantages of Thermocouple
- High accuracy
- Low Cost
- Wide operating temperature range
Disadvantages of Thermocouple
- Non-linearity
- Low voltage
- Recalibration is difficult
Thermocouple Applications
- Industries where an accurate and huge range of temperatures required.
- Thermostats in offices, homes, and businesses.