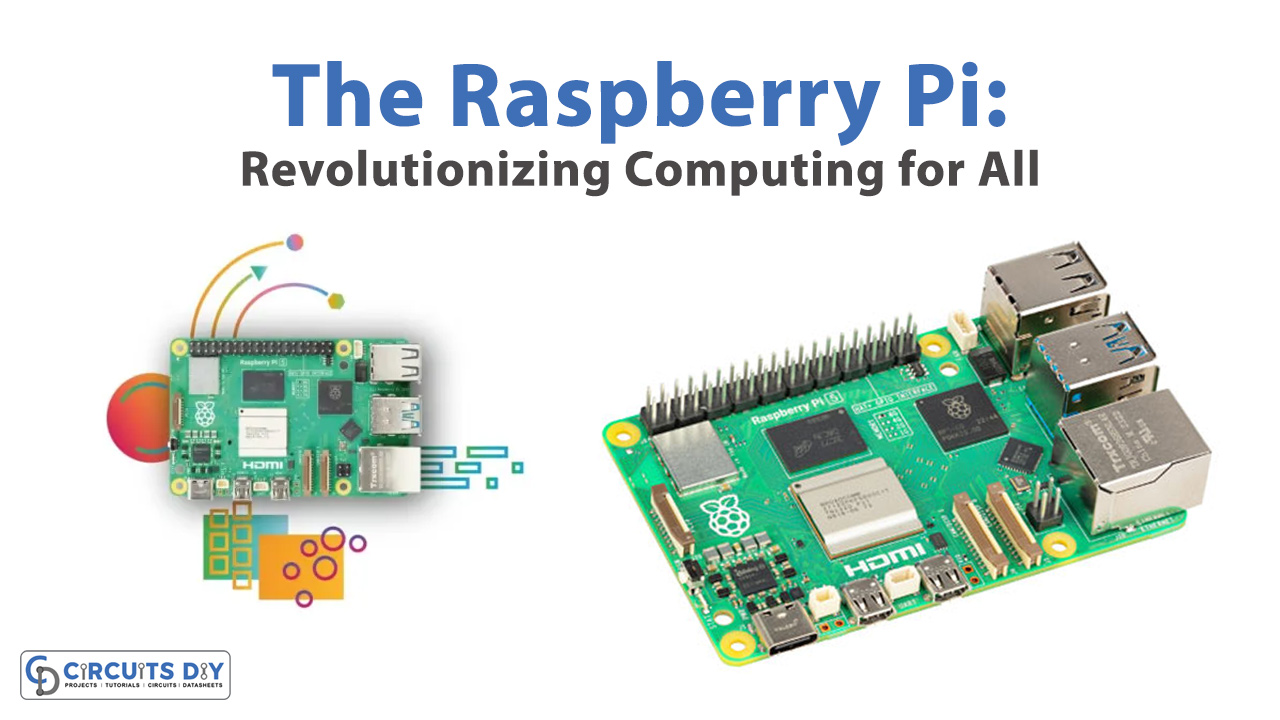
In the realm of affordable and versatile computing, the Raspberry Pi stands as a game-changing innovation. Launched in 2012 by the Raspberry Pi Foundation, this single-board computer has transformed from a simple educational tool into a global phenomenon, catering to hobbyists, educators, and professionals alike. Let’s explore the origins, evolution, and diverse applications of this remarkable device.
Origins and Evolution
The Raspberry Pi was conceived with a clear mission: to promote computer science education and provide accessible computing to everyone. The brainchild of Eben Upton and his team at the University of Cambridge, the first Raspberry Pi model (Raspberry Pi Model B) was launched in February 2012. Priced at $35, it featured a 700 MHz ARM11 processor, 256 MB of RAM, and basic connectivity options, making it an affordable and capable entry point into the world of computing.
Since its inception, the Raspberry Pi has undergone several iterations, each improving upon the last. The introduction of the Raspberry Pi 2 in 2015 brought a quad-core ARM Cortex-A7 processor and 1 GB of RAM, significantly boosting performance. The Raspberry Pi 3, released in 2016, added built-in Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, enhancing its connectivity. The latest iteration, the Raspberry Pi 5, offers up to 8 GB of LPDDR4X RAM (4267 MHz), 2x USB-A 3.0 (5 GBit/s) & 2x USB-A 2.0, and dual 4K display output, rivaling many traditional desktop computers in capability while retaining its compact form factor and affordability.

Raspberry Pi 5 Features
- 64-bit quad-core ARM Cortex-A76 processor (2.4 GHz)
- VideoCore VII GPU (800 MHz)
- 8 GB of LPDDR4X RAM (4267 MHz)
- Raspberry Pi silicon RP1 I/O controller chip
- Real-time clock
- On/off button
- PCIe 2.0
- UART connector
- Fan connector
Technical Specifications
| SoC | Broadcom BCM2712 |
| CPU | ARM Cortex-A76 (ARM v8) 64-bit |
| Clock speed | 4x 2.4 GHz |
| GPU | VideoCore VII (800 MHz) |
| RAM | 8 GB LPDDR4X (4267 MHz) |
| WiFi | IEEE 802.11b/g/n/ac (2.4 GHz/5 GHz) |
| Bluetooth | Bluetooth 5.0, BLE |
| Ethernet | Gigabit Ethernet (with PoE+ support) |
| USB | 2x USB-A 3.0 (5 GBit/s) 2x USB-A 2.0 |
| PCI Express | 1x PCIe 2.0 |
| GPIO | Standard 40-pin GPIO header |
| Video | 2x micro-HDMI ports (4K60) 2x 4-lane MIPI (DSI/CSI) |
| Multimedia | H.265 (4K60 decode) OpenGL ES 3.1, Vulkan 1.2 |
| SD card | microSD |
| Power | 5 V/5 A (via USB-C) Power over Ethernet (PoE+) |
Educational Impact
At its core, the Raspberry Pi was designed to foster an interest in computer science and programming among young people. Its low cost and versatility make it an ideal platform for educational institutions and hobbyists to explore coding, electronics, and computer hardware. The Raspberry Pi Foundation supports this mission through various initiatives, including online resources, coding clubs, and the distribution of free educational materials.
Programs like Code Club and CoderDojo have leveraged the Raspberry Pi to teach coding to children in a hands-on and engaging manner. Additionally, the inclusion of the Scratch programming language and the Python language on the Raspberry Pi OS (formerly Raspbian) allows beginners to start coding with ease.
Versatility and Applications
Beyond education, the Raspberry Pi has found applications in numerous fields due to its affordability, small size, and robust performance. Some notable uses include:
- Home Automation: The Raspberry Pi can serve as the brains behind home automation systems, controlling lights, thermostats, and security cameras.
- Media Centers: With software like OSMC or Plex, the Raspberry Pi can be transformed into a powerful media center capable of streaming and playing high-definition content.
- IoT Projects: Its GPIO pins make it ideal for Internet of Things (IoT) projects, enabling users to connect sensors and actuators for various applications like weather stations, smart agriculture, and more.
- Retro Gaming: Emulators and software packages like RetroPie allow the Raspberry Pi to become a retro gaming console, playing classic games from various consoles.
- DIY Projects: Makers and tinkerers use the Raspberry Pi for countless DIY projects, from building robots to creating custom computer interfaces.
Future Prospects
The future of the Raspberry Pi looks promising as it continues to push the boundaries of what affordable computing can achieve. Upcoming advancements may include more powerful hardware, enhanced AI capabilities, and further integration into educational curriculums worldwide. The Raspberry Pi Foundation’s commitment to open-source software and hardware ensures that it will remain a cornerstone of innovation and accessibility in computing.
In conclusion, the Raspberry Pi has revolutionized the way we perceive and utilize computing devices. From its humble beginnings as an educational tool to its current status as a versatile and powerful platform, it exemplifies the potential of accessible technology to inspire, educate, and innovate. As we look ahead, the Raspberry Pi will undoubtedly continue to be a catalyst for creativity and learning, empowering individuals and communities around the globe.
Download Raspberry Pi 5 Datasheet