In the realm of modern technology, electronic components are the unsung heroes that power our devices and facilitate the seamless flow of information. From the simplest circuits to complex systems, these components form the fundamental building blocks that enable the functioning of electronics devices across various industries. Let’s delve into the world of electronic components to understand their importance, types, and applications.
Importance of Electronic Components
Electronic components are essential elements that perform specific tasks within an electronic circuit. They can be passive, such as resistors and capacitors, or active, like transistors and integrated circuits (ICs). Each component serves a unique purpose, contributing to the overall functionality and performance of electronic devices.
For instance, resistors regulate the flow of electric current, capacitors store and release electrical energy, transistors act as switches or amplifiers, and ICs integrate multiple functions into a compact package. Without these components, electronic systems would be non-functional or inefficient, highlighting their critical role in modern technology.
Types of Electronic Components
1. Passive Components
Passive components do not require an external power source to perform their function. Some common passive components include:
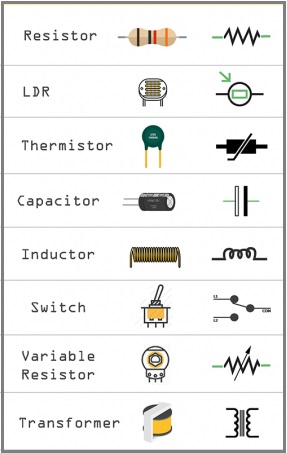
- Resistors: Control the flow of electric current.
- Capacitors: Store and release electrical energy.
- Inductors: Store energy in a magnetic field.
- Diodes: Allow current to flow in one direction only.
- Transformers: Transfer electrical energy between circuits through electromagnetic induction.
2. Active Components
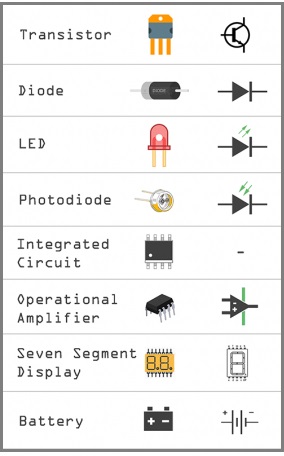
Active components require an external power source to operate and can amplify or control electric signals. Examples of active components include:
- Transistors: Act as switches or amplifiers in electronic circuits.
- Integrated Circuits (ICs): Combine multiple electronic components into a single package.
- Operational Amplifiers (Op-Amps): Amplify differential voltage signals.
- Microcontrollers: Control and manage various functions within electronic systems.
3. Electromechanical Components
These components integrate electrical and mechanical functionalities, bridging the gap between electrical circuits and physical movement. Examples include:
- Relays: Electrically controlled switches.
- Motors: Convert electrical energy into mechanical motion.
- Sensors: Detect and respond to environmental stimuli.
Applications of Electronic Components
Electronic components find applications across diverse industries and sectors:
- Consumer Electronics: Smartphones, laptops, TVs, and home appliances utilize various electronic components for functionality and connectivity.
- Automotive Industry: Vehicles incorporate electronic components for engine control, navigation systems, entertainment, and safety features.
- Industrial Automation: Electronic components are integral to automated manufacturing processes, robotics, and control systems.
- Medical Devices: Electronic components play a crucial role in medical equipment such as MRI machines, pacemakers, and diagnostic devices.
- Communications: Telecommunication networks rely on electronic components for data transmission, networking, and signal processing.
Future Trends and Innovations
The field of electronic components is continuously evolving, driven by advancements in materials, miniaturization, and integration technologies. Key trends and innovations shaping the future of electronic components include:
- Miniaturization: Components are becoming smaller, enabling compact and portable devices.
- IoT Integration: Components are designed to support the Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem, enabling interconnected and smart devices.
- Flexible Electronics: Flexible and stretchable components open up new possibilities for wearable technology and flexible displays.
- Advanced Materials: Emerging materials such as graphene and nanomaterials offer enhanced performance and functionality.
- Energy Efficiency: Components are designed with a focus on energy efficiency and sustainability.
Wrapping up
Electronic components form the backbone of modern electronics, driving innovation, connectivity, and functionality across industries. Understanding the types, functions, and applications of these components is essential for anyone involved in electronics design, manufacturing, or maintenance.