Introduction
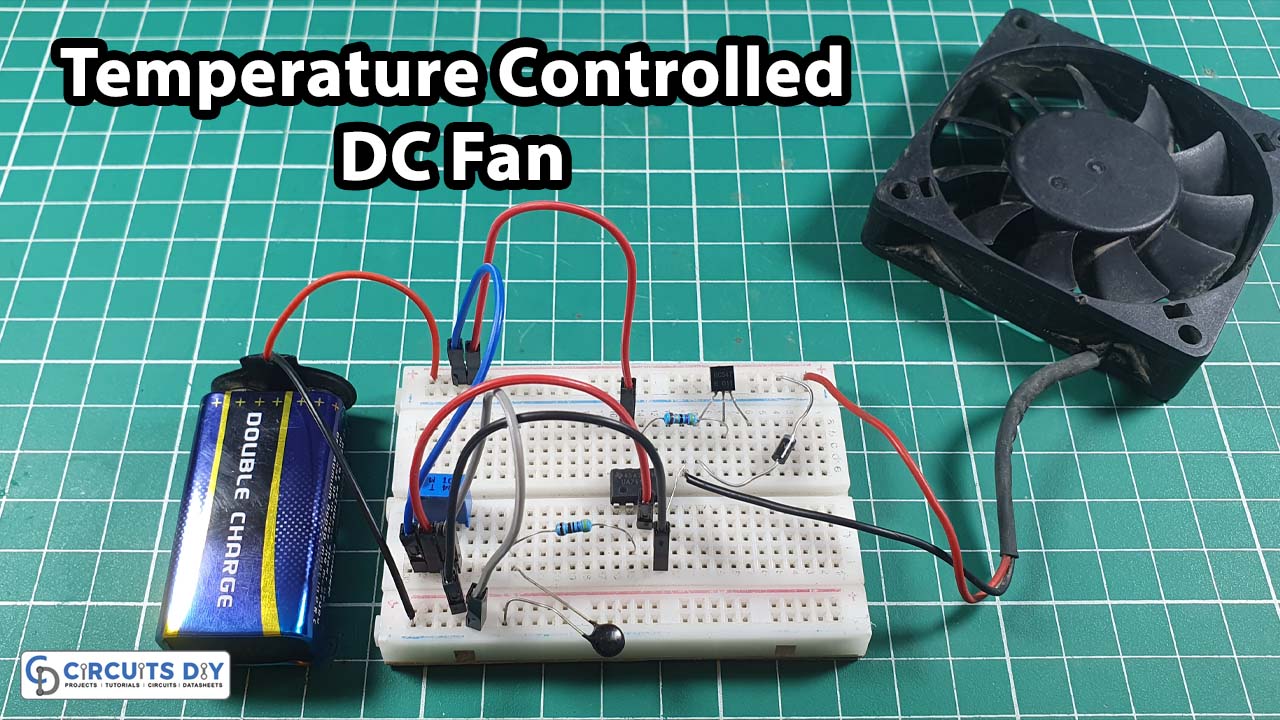
Nobody needs us to explain the importance of fans in our lives. Hey! I am talking about the electrical fans. The ones most of us cannot live without. But nobody can deny the fact that many countries are still fighting load-shedding issues. And, many of them have bad weather, the intolerable unbearable higher temperature makes the situation worst. What if we make a DC fan for those conditions that don’t require electricity? Just a DC battery and a few different electronic components. Sounds good? so let’s make this circuit. Now. in this tutorial, we are going to “Temperature Controlled DC Fan”
Hardware Components
The following components are required to make Temperature Controlled DC Fan Circuit
| S.no | Component | Value | Qty |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Thermistor | 10KΩ | 1 |
| 2. | Operational Amplifier IC | LM741 | 1 |
| 3. | DC Fan | 9V | 1 |
| 4. | Transistor | BC547 | 1 |
| 5. | Potentiometer | 10KΩ | 1 |
| 6. | Diode | 1N4007 | 1 |
| 7. | Resistor | 4.7KΩ, 39Ω | 1,1 |
| 8. | 2 Pin Connector | 2 |
LM741 Pinout
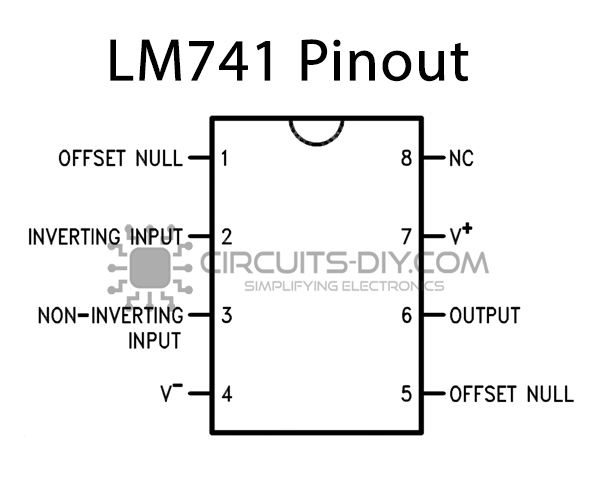
For a detailed description of pinout, dimension features, and specifications download the datasheet of LM741
Temperature Controlled DC Fan Circuit
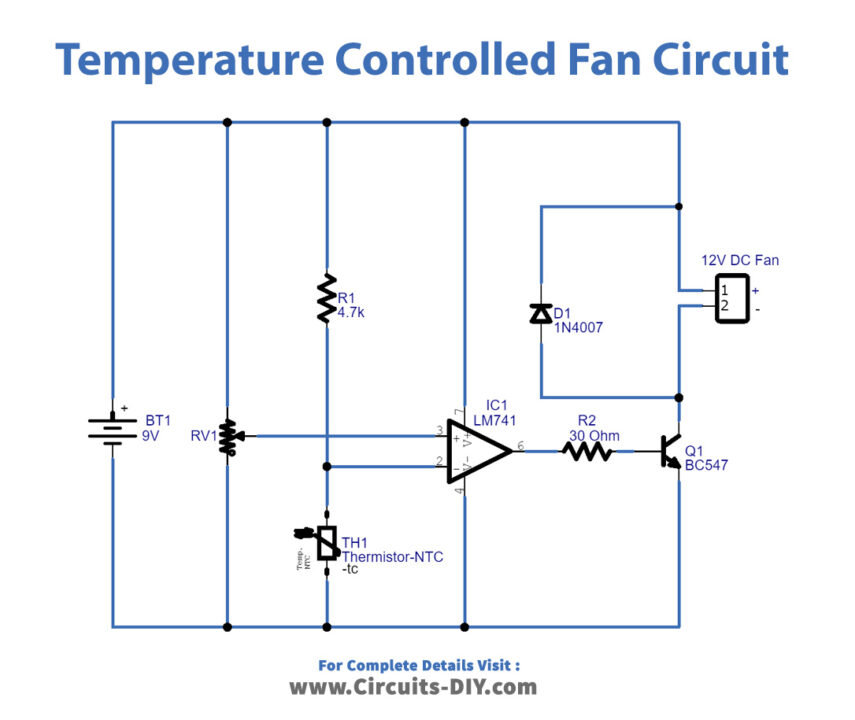
Working Explanation
In this Temperature Controlled DC Fan, we are using an Operational Amplifier as our major component which first compares reference voltage at the inverting and non-inverting input pins and controls the output voltage. Transistor BC547 is working as a switch that makes connections DC fan from the power supply. There is also connected a potentiometer in the circuit which is wired across the power supply and its variable pin to the Noninverting input of IC.
When the temperature of the surroundings increases and attains the threshold, then the operational amplifier gives differential voltage turns ON the transistor. As a result, the connected DC fan gets ground supply and runs. If the temperature level goes below the set threshold level, then op-amp IC produces zero output, hence Q1 remains in OFF condition and so does the DC fan.
Application and Uses
- Ventilation devices
- Cooling systems
- Power generation circuits
- Dust collection device, etc