Introduction to Flexible Printed Circuit Board
As the years are passing and technology is evolving, printed circuit boards are also evolving day by day. Since different kinds of devices needed different types of PCBs. Therefore, designers worked hard and made several classifications of PCBs. And, Flexible PCBs are one of that type. The devices that require maximum availability and reliability use flex PCBs. That’s why the substrate material used in the Flexible Printed Circuit Board plays a significant role in its making.

Brief Overview of Flexible Substrate
A flexible substrate is a very thin material. And, this usually uses polyimide and polyethylene terephthalate for its making. They are used because of their impressive electrical and thermal properties. The thickness of the material is between 12 to 125um. This is equal to 0.5 to 5 mils. Moreover, this substrate helps to mold the shape in any form. Yet, it is only possible during the manufacturing process. Also, it enables the flexible bend of the PCB.
Elements of Flex Substrate Material
The material works efficiently with the other elements used in the manufacturing process of flex PCBs. Below is some explanation of the function of those elements:
- Base Material: Base material provides the foundation for lamination. As we explained earlier that it uses a thickness between 12 to 125 um. But, thicker and thinner materials can be used. However, the thinner materials are more flexible. For instance, if the material is double in thickness, the material will be the eight-time stuffer. Furthermore, there are several materials for this purpose. But, mostly polyamide films are utilized because of their thermal, electrical, chemical, and other properties
- Bonding Adhesive: Adhesives are the bonding medium for lamination. Like the base material, they come in different thicknesses. And, the application decides the material thickness according to its requirement. While, On the one hand, they are common. The creation of cover layers. On the other hand, they are not very temperature resistant
- Metal Foil: It is the conductive element of the circuit. Circuit paths etch through this metal foil. They also come in various thicknesses. Usually, foil material uses copper as a metal foil in flex PCBs
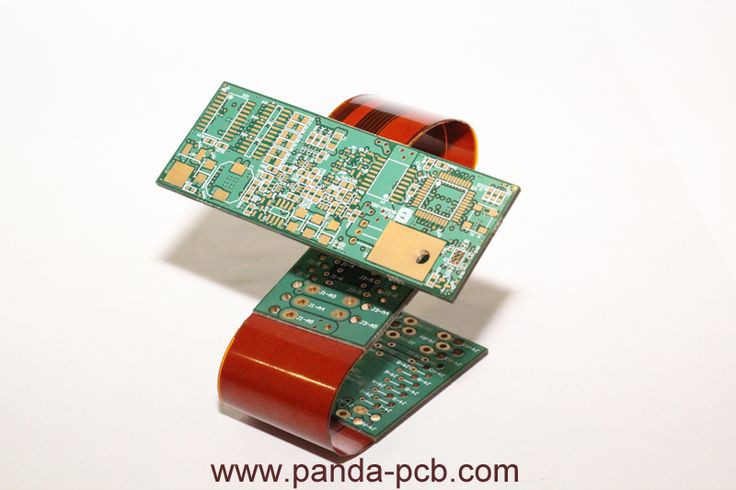

Manufacturing Process of Flex Substrate
The manufacturing process of flex substrate flows as:
- Firstly, it built a conductive layer by using a metal buffer on the polyamide substrate
- Then, the process utilized the image transfer technology for anti plating fry film pattern on the buffer layer
- Further, it uses a graphic electroplating process for the thickness of copper on the conductor line
- Lastly, it does the etching process for the fabrication
Applications of Flexible Substrate and Printed Circuit Board
The application of flexible printed circuit boards is increasing as time passes. For example, advanced optoelectronic devices, it is playing a crucial role. It is highly utilized in biomedical sensors. Robotic devices also prefer flex PCBs. Moreover, mobile devices often use these PCBs effectively. Hence, the substrate material is an important factor in many electronic devices and equipment. So, it is to ensure to use the best quality material or to choose the best manufacturer for your device’s need. Also, it is critical yet valuable to find the thickness of the material for your application. This is necessary for the optimal durability rate and reliability of the device.