With the continuous advancement in small scale electronic product integration. many PCB fab houses are modifying themselves to be able to process small SMD components. SMT components are usually much smaller than their THT counterparts, usually because of their smaller or no leads at all. Surface mount technology was initially introduced back in the late 1960s as planar mounting equipment and by the 1990s, became a mandatory implication in consumer electronics. There are many different kinds of SMD parts available in today’s market, with very slight visual differences. So, it is quite understandable that the concept of selecting and using SMDs might be a bit daunting for newbies. This article will serve as a complete guide for beginners to SMD components. All the while also helping them in identifying different SMD parts.
What are SMD Components?
Surface Mount Devices or SMDs are components that manufacturers and technicians use to mount on SMT PCBs. All SMDs operating on a PCB work in unison in order to make up a functioning circuit. SMD components require less space as compared to the conventional THT parts. They also make it very easy to mass solder. There are a wide variety of SMD parts available in today’s market, some of them which we’ll be discussing today.
JLCPCB is the foremost PCB prototype & manufacturing company in china, providing us with the best service we have ever experienced regarding (Quality, Price Service & Time).
Commonly Used SMD Footprint Parts & Their Identification
1) Chip Resistors (R)
Chip Resistors are the most common SMD parts that manufacturers use on SMT PCBs. Usually, the 3 numbers on the body of a chip resistor show its resistance value. the 1st and 2nd digits are significant digits, and the 3rd digit indicates the multiple of 10, such as “105” indicates “1MΩ”, “672” is “6.7KΩ”. The letter “R” refers to a decimal point, for example, “R15” means “0.15Ω”.

2) Network Resistor (RA/RN)
Network resistor chips are basically high grade ceramics with internal metal electrodes on each end to make the contacts to the thick film resistive element. The chip usually packages several resistors with the same parameters together. Their identification method is as same as chip resistors. They are usually used in digital memory circuits.

3) Ceramic Capacitors (C)
An SMD capacitor usually consists of a rectangular block of ceramic dielectric, containing a number of interleaved metal electrodes. The inner electrodes are connected to the two end terminations and are covered with a layer of plated tin (NiSn). PCB Manufacturers usually use MLCC SMDs. MLCC has further three types: COG(NPO), X7R & Y5V, out of which COG (NPO) is the most stable.

4) Diode (D)
The internal structure of an SMD diode is basically the same as that of a general purpose diode. The identification of +ve and -ve poles of an SMD diode is on the SMD diodes casing. Generally, on the body of the diode, the color ring marks the direction of its -ve pole.

5) LED
SMD LED consists of three cells that contain a luminescent element (Semiconductor crystal) that produces light when a current flows through it. The determination of an SMD LED polarity is done by the specific product manufacturing guideline.

6) Transistors (Q)
In SMD transistors, the resistance is built in the base and the ammeter. SMD transistors are also known as RET (Resistance equipped transistors). The most used packages in SMD components are SOT-23 and SOT-223 (larger). No matter the production code, every SMD transistor identifies by the first two Alphabets on the body of its SMD.

First Alphabet:
- A= Germanium
- B = Silicon
- C = Gallium Arsenide
- D = Indium Antimide
Second Alphabet:
- C = Audio Frequency Amplifier
- D = Audio Frequency Power Amplifier
- F = Low Power Radio Frequency Amplifier
- P = High Power Radio Frequency Amplifier
7) Inductors
SMD inductors are +ve reactance devices and are available in many different sizes and form factors. Their values are usually on their SMD casing.
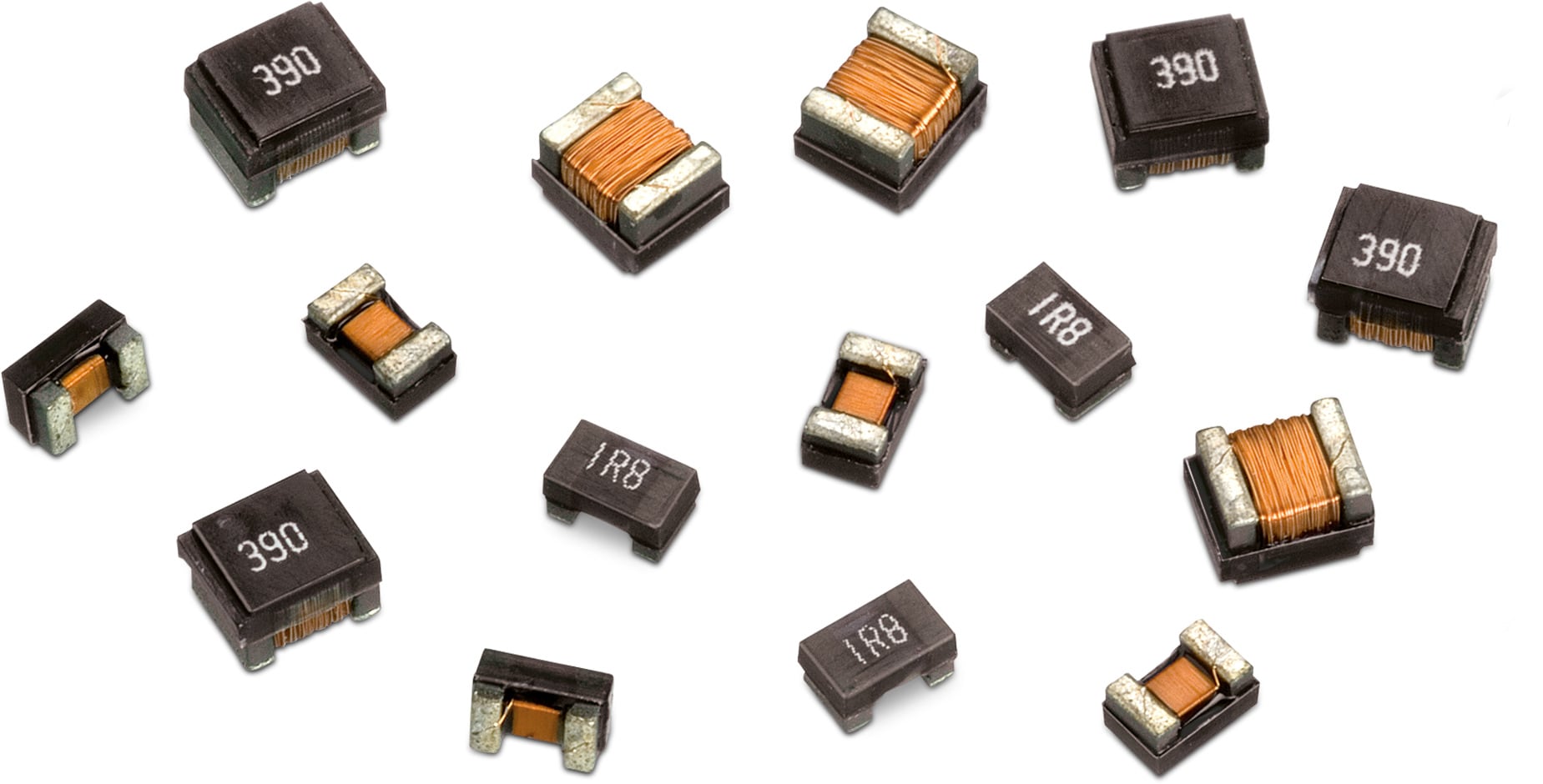
8) SMD Transformers (T)
SMD transformers are usually wound on toroidal cores. With surface mount headers for PCB connections. Their designs vary widely in terms of power rating, voltage and current levels, size, impedance, bandwidth, packaging, winding capacitance, and other parameters.

9) Crystal OScillators (X)
SMD crystal oscillators mainly serve the function of generating oscillation frequency in various circuits.

10) IC (U)
SMD IC packages are available in various packages. A few to name are SOP, SOJ, PLCC, LCCC, QFP, BGA, CSP, FC, MCM, and so on. The most complex of them is the BGA SMD chip with very high pin density. Since, the pins are spherical and have a small contact surface with the PCB pads, the requirements for SMT are more precise.