Introduction
A continuity test is important for any circuit. One broken wire can damage the whole circuit. The continuity test, as the name implies, examines the current continuity. In basic terms, it determines if the current is easily flowing from one end to the other. The purpose of continuity testing is to see if there is an open track on a circuit board or if there is a break in a wire. It can also tell whether a track or wire has been shortened to connect to another track or cable. And, to test this continuity there are different circuits and devices; for example, a multimeter. But, in this tutorial, we are going to make a “Simple continuity tester circuit diagram”.
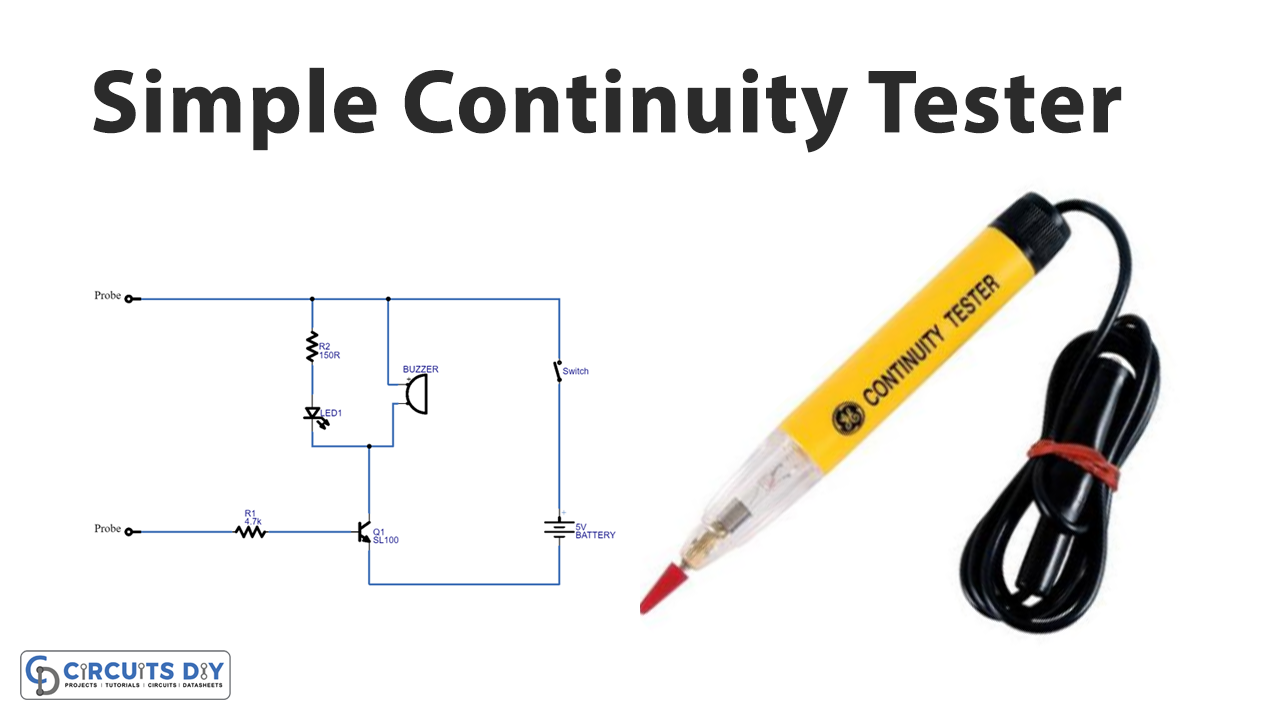
When continuity is present at the probes, this basic continuity tester circuit, built with a single NPN switching transistor SL100, will provide visual and audible outputs.
Hardware Components
The following components are required to make the Continuity Tester Circuit
| S.no | Component | Value | Qty |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | NPN Transistor | SL100 | 1 |
| 2. | Buzzer | – | 1 |
| 3. | Switch | – | 1 |
| 4. | Battery | 5v | 1 |
| 5. | Resistor | 150Ω, 4.7KΩ | 1, 1 |
| 6. | LED | – | 1 |
SL100 Pinout
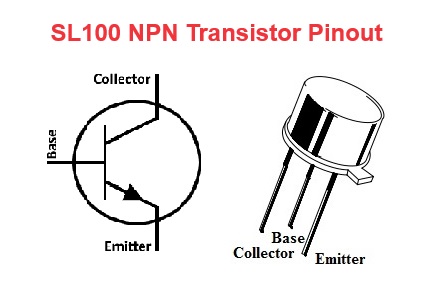
For a detailed description of pinout, dimension features, and specifications download the datasheet of SL100
Continuity Tester Circuit
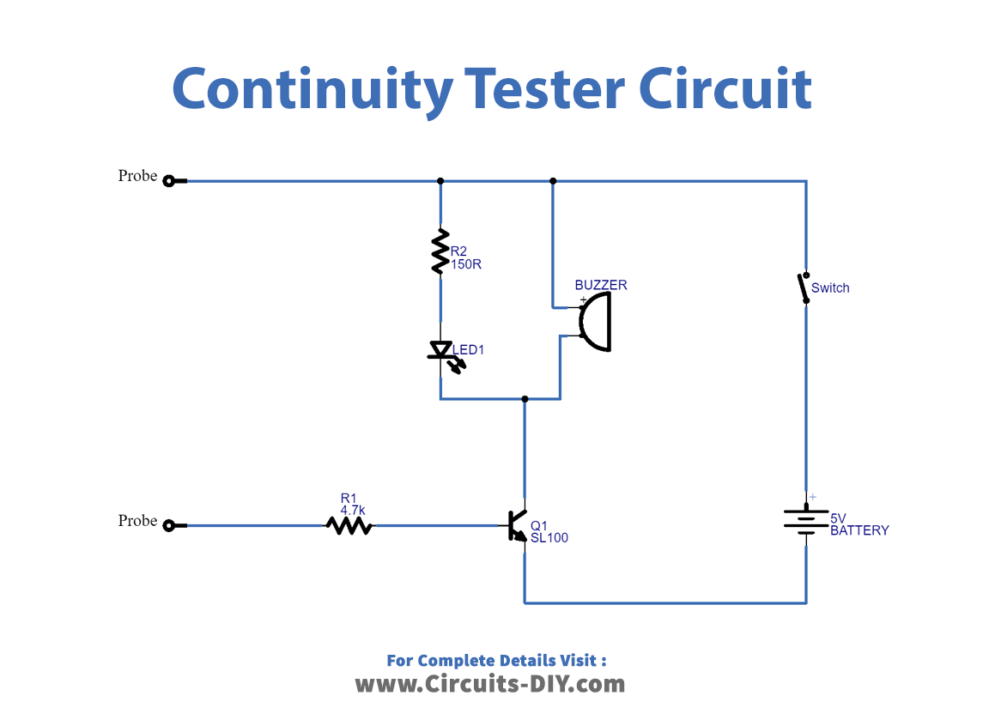
Working Explanation
In this Simple continuity tester circuit diagram, we have used the SL100 NPN transistor having switching characteristics. The collector terminal of the transistor is wired to the 5V supply through a buzzer and an LED, while the emitter terminal is directly connected to the negative end of the battery. When the minimal bias voltage, which is 0.7V s applied to the base pin, the SL100 transistor acts as a closed switch, and the LED and Buzzer provide output, allowing us to determine the continuity between the two probes.
Application and Uses
- To test the continuity of the different circuits.