Introduction
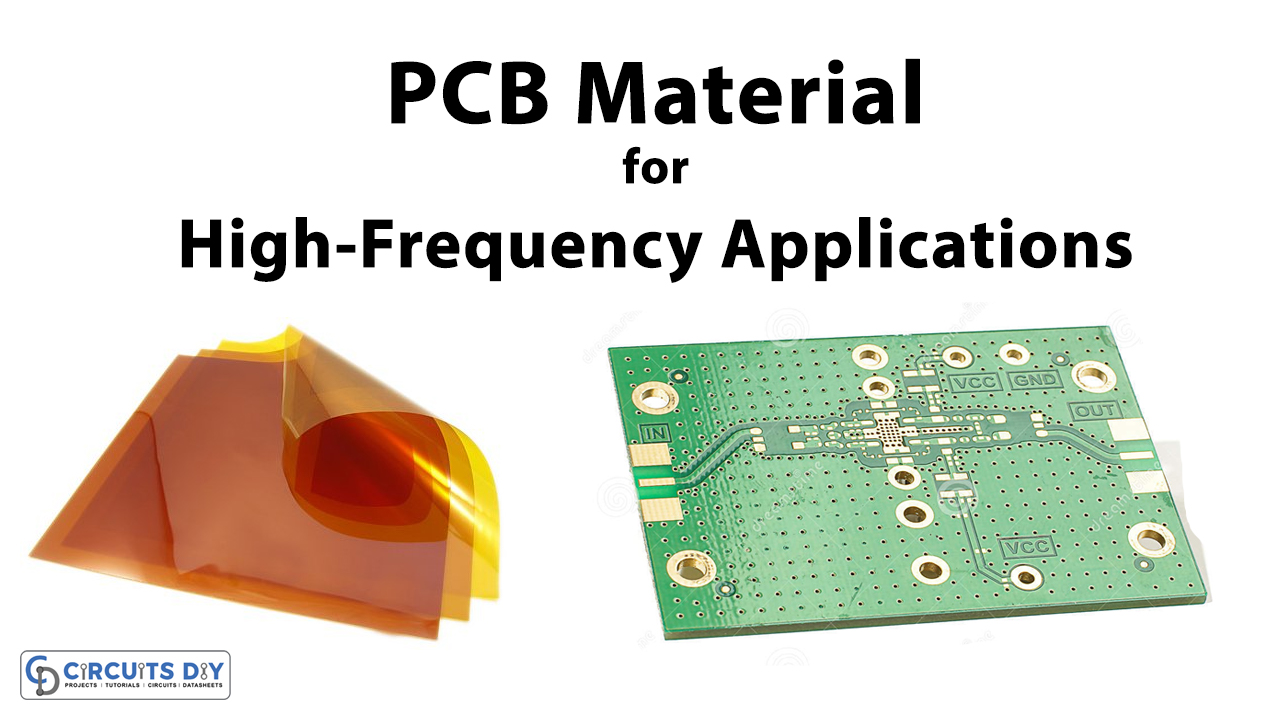
Generally, the Printed circuit boards (PCB) use cost-effective FR-4 material for their products. This Flame Retardant material is easy to handle, therefore used widely. But, the high-frequency application requires high performance and stability. Hence, this is not achieved by FR-4 material. We can not deny the fact that FR-4 has limitations for high power, heat, and voltage. So, when the circuit exceeds those limits, the dielectric properties of this material start to decline. And, therefore, the insulating property of the material starts to break down. This, allow a high current to flow which can damage the circuit and so the printed circuit board.

High-Frequency Application Requirements
High-frequency applications require some factors to consider before choosing the material. These factors are:
- Dimensional stability
- controlled impedance
- Less moisture absorbtion
- High performance
- Thermal management
- Low attenuation ( for wireless communication)
- adaptive permittivity ( for wireless communication)
- Homogenous construction ( for wireless communication)
Materials for High Frequency
While choosing the material for high-frequency applications, it is imperative to list down some factors that need to be addressed. These factors include impedance, performance, stability, moisture, thermal management, etc. Below we are briefly discussing the material to describe these factors.
- For Dimensional Stability: To maintain dimensional stability, a PCB design requires great physical tolerance. Therefore, hydrocarbons laminate material is one of the best choices for this purpose.
- For controlled Impedance: The high-frequency applications that require controlled impedance and routing can use polytetrafluoroethylene for this purpose. Moreover, the enhanced epoxy can also be utilized to control the impedance. Both the materials hold the dielectric constant tolerance of 2%.
- For Decreased Moisture: Moisture absorbed rating can also be considered while selecting the material for high-frequency boards. Since the small amount of moisture absorption can generate a lot of effects on the boards. that’s why it is necessary to address this. Typical Fr-4 can absorb the moisture of 50%, while polytetrafluoroethylene absorbs the least moisture of 2%. Hence, recommended using.
- For High Performance: As the frequency increases, the problem can arise between the transmission lines and it can cause the signal to lose. So, enhanced epoxy orPTEE materials are preferable.
- For Thermal Management: High-frequency applications generate a high amount of heat which can cause damage to the board if the material is not selected well. To overcome this issue, polyimide is the best material to use.
Cost Consideration
On one hand, we can say that high-frequency materials have high performance, high stability, and durability rate. On the other hand, we cannot disavow the fact that it can cost higher more than other simple PCB materials. Hence, it is difficult to find the best material is very low and cheap prices for high frequency. Also, high-frequency materials are often difficult to handle or work with. However, you can consult your manufacturer for this purpose.
Conclusion
So, in this article, we have seen the factors that are considered for the high frequency. Forward, we have discussed the materials that are used for high-frequency applications. Through that discussion, we have comprehended that high-frequency applications can cost higher but are more durable and efficient.