Introduction
Have you ever faced a situation where you need to charge multiple batteries together, but the charger only has a single output? Or have you ever wondered how to switch between different batteries for powering up your devices without creating a mess? Look no further as we introduce a super innovative parallel battery charger/changeover circuit using SPDT switches.
This circuit allows you to charge multiple batteries separately or together and switch between them easily, all while ensuring a safe and efficient charging and discharging process. So, let’s dive into the world of circuitry and explore this exciting design!
Circuit Diagram

Working Explanation
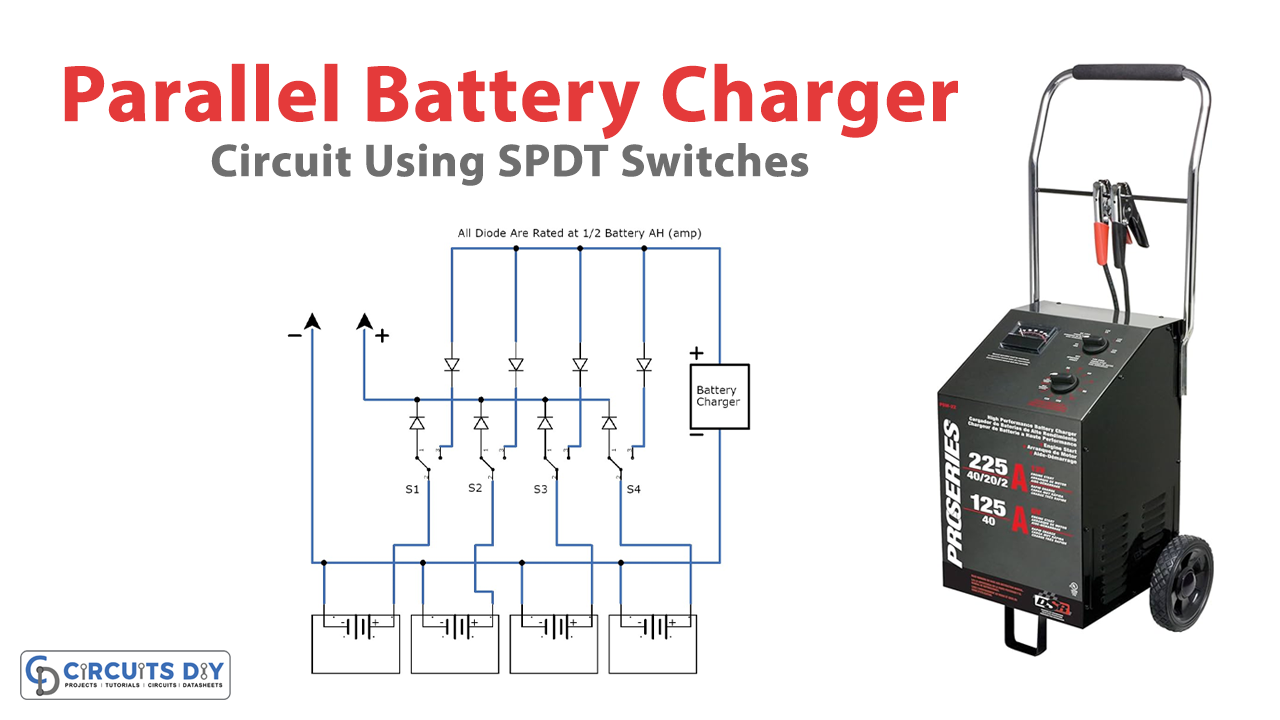
The circuit comprises four batteries, each with negative terminals connected to form a common negative rail. The positives of the batteries are connected to four discretely connected SPDT switches, allowing each battery to be switched on/off independently. One of the two changeover contacts of the SPDT switches is connected to the output load, while the others are connected to the positive terminal of the battery charger.
To prevent cross-discharge between the batteries, each battery positive terminal and the output load are connected to a separate rectifier diode. Similarly, the battery charger positive is connected to a separate rectifier diode to ensure that the batteries do not get to know one another and create a cross-discharge across each other.
The diodes also ensure a step-wise charging and discharging process for each battery. The current flows through the diode with the highest voltage, gradually charging each battery.
When you want to charge multiple batteries simultaneously, all you need to do is switch on the SPDT switches connected to the batteries you want to charge, and the charging current will flow through those batteries. If you only want to charge a single battery, you can switch off the other SPDT switches.
Similarly, when you want to power up your device using one of the batteries, you can switch on the SPDT switch connected to that battery, and the output load will receive power from that battery. If you want to switch to a different battery, switch off the first SPDT switch and switch on the one connected to the battery you want to use.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the parallel battery charger/changeover circuit using SPDT switches is an efficient and cost-effective way to charge multiple batteries. With the use of a single battery charger and manual switches, you can charge the batteries separately or together in a parallel connection. This circuit design offers flexibility and convenience for managing your batteries, ensuring proper charging and discharging without damaging them.
So, if you’re looking for a simple yet effective way to charge multiple batteries, try this circuit and see the difference it makes!