Overview
In today’s tutorial, we’ll be creating a small and portable NiCd Battery Charger Circuit with Reverse Polarity Protection that can charge multiple batteries simultaneously.
NiCd Batteries?
NiCd batteries, short for nickel-cadmium batteries, are a type of rechargeable battery that uses nickel oxide hydroxide and metallic cadmium as electrodes. They are known for their ability to provide a reliable and stable source of power, especially in applications requiring high discharge rates. NiCd batteries are commonly used in portable electronic devices, power tools, and various industrial applications due to their durability, long cycle life, and consistent performance.
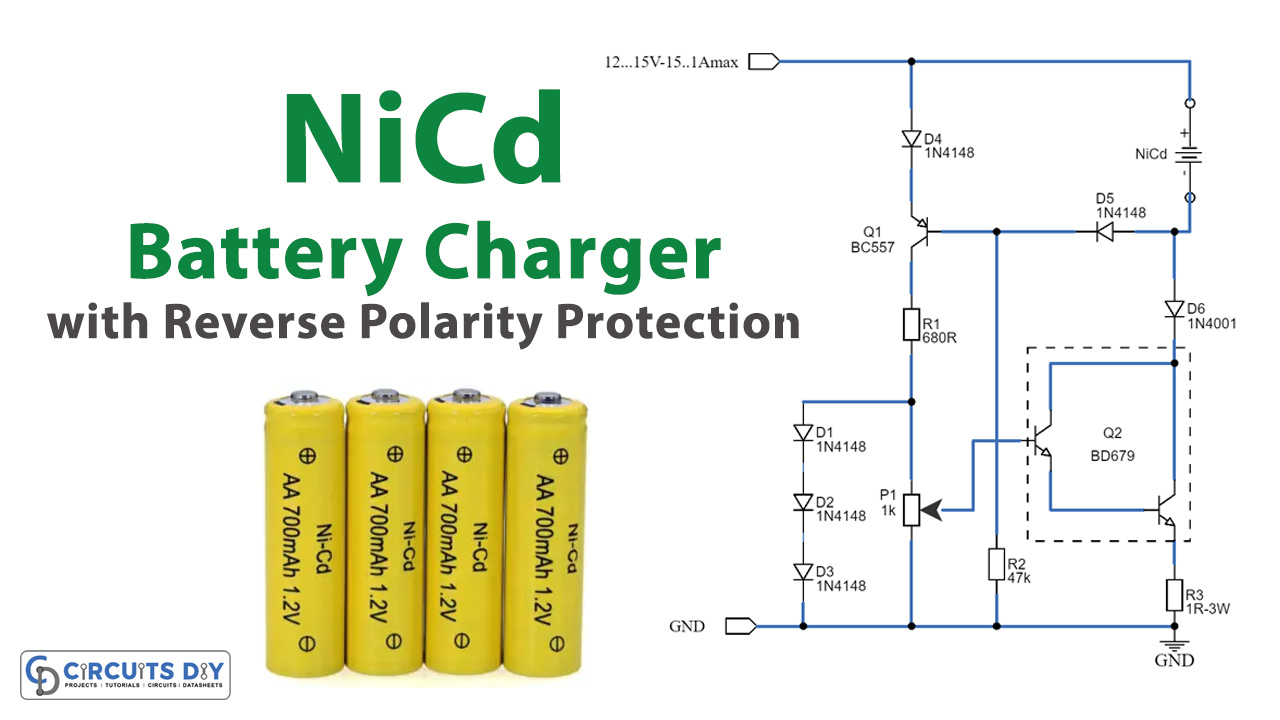
This NiCd battery charger is engineered for charging up to 7 NiCd batteries linked in series. Additional battery capacity can be augmented by elevating the power supply by 1.65V per extra battery. When Q2 is affixed to a suitable heatsink, the input voltage can be elevated to a maximum of 25V. Unlike many commercial NiCd chargers in the market, this charger includes reverse polarity protection. Another notable attribute is its capability to prevent battery discharge upon disconnection from the power source.
Typically, NiCd batteries necessitate a 14-hour charging duration at a current equivalent to one-tenth of their capacity. For example, a 500 mAh battery would be charged at 50 mA for 14 hours. Excessive charging current can lead to battery damage. The charging current level is adjustable via P1 within the 0 mA to 1000 mA range. Q1 triggers when the NiCd battery is connected with the correct polarity or when the output terminals are vacant. Q2 necessitates being mounted on a heatsink. In the absence of a BD679, it can be replaced with any NPN medium-power Darlington transistor meeting the 30V and 2A output criteria. Reducing the value of R3 increases the maximum output current to up to 1A.
Hardware Components
You’ll need the following hardware components to get started:
| S.no | Components | Value | Qty |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Diodes | D1-D5 = 1N4148 D6 = 1N4001 | 1 1 |
| 2 | Transistors | Q1 = BC557 Q2 = BD679 (Darlington) | 1 1 |
| 3 | Potentiometer | P1 = 1K | 1 |
| 4 | Resistors | R1 = 680R R2 = 47K R3 = 1R-3W | 1 1 1 |
Schematic
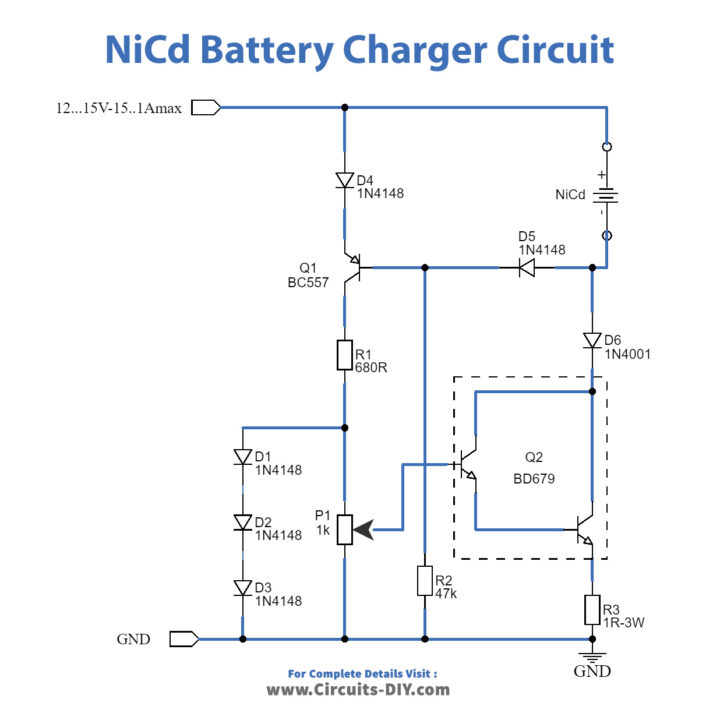
Working Explanation
asdad
Applications
NiCd batteries are used in our so many daily life gadgets
- Portable electronic devices such as flashlights, radios, and portable music players
- Power tools like cordless drills, screwdrivers, and saws
- Emergency backup systems for lighting and communication devices
Conclusion
This “NiCd Battery Charger Circuit” represents a significant advancement in battery charging technology, offering a reliable and efficient solution for powering multiple NiCd batteries while safeguarding against potential damage from reverse polarity.