Introduction
Do you want a simple yet precise solution to charge all kinds of NiCd batteries with great accuracy? This blog post is the answer to your needs! In this post, we will discuss a simple IC 555-based NiCd charger circuit that can generate a voltage higher than the nominal voltage required to charge the battery. This circuit maintains a safe and suitable charging current for NiCd batteries, ensuring their longevity and efficiency.
So, let’s dive into the details of this innovative NiCd battery charger circuit and see how it can revolutionize your battery charging experience!
Hardware Required
| S.no | Components | Value | Qty |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | IC | NE555 , 78L05 | 1 |
| 2 | Capacitor | 10n | 2 |
| 3 | Resistor | 10k, 680R | 2, 1 |
| 4 | Diode | 1N4148 | 4 |
| 5 | LED | Red | 1 |
| 6 | Polar Capacitor | 1uF 16V | 2 |
| 7 | Battery | 12 | 1 |
Circuit Diagram
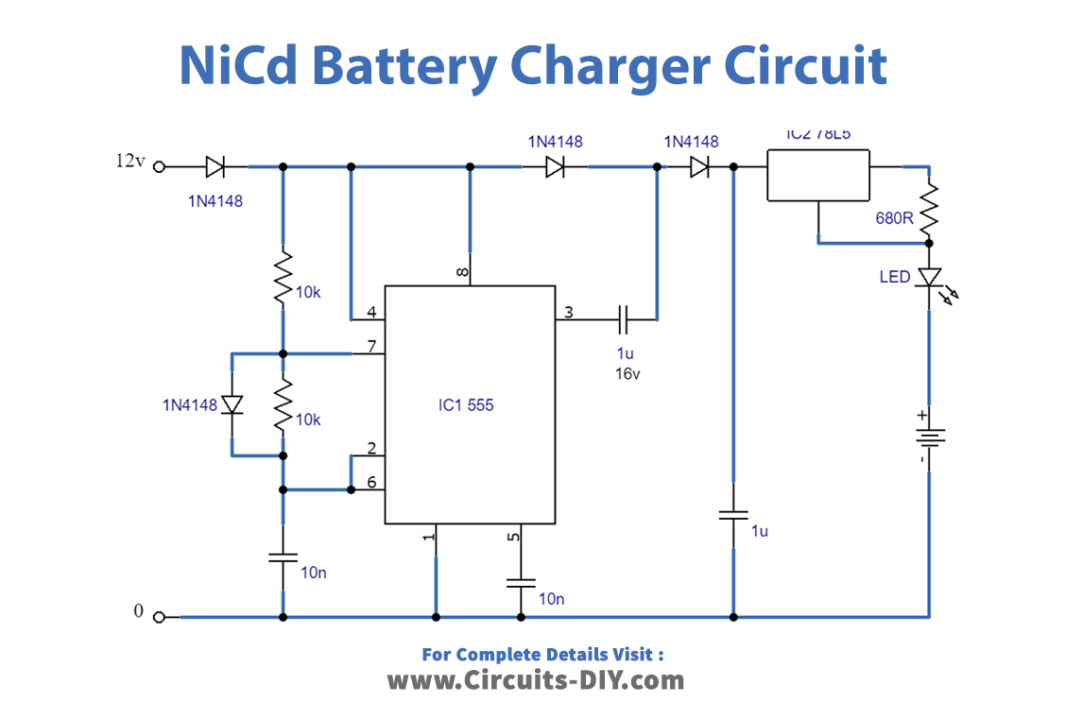
Circuit Explanation
This NiCd battery charger circuit is essentially a voltage doubler constructed from the IC 555. The IC generates an oscillation that alternately connects the circuit’s output to the earth and the 12 V supply voltage. When the output of the IC is at a low logic level, diodes D2 and D3 charge capacitor C3 to around 12 V. When the output is at a high logic level, the voltage at the junction of C3 and D3 doubles to almost 24 V, as C3’s negative terminal is at +12 V. This doubles the voltage required to charge the NiCd battery.
The 78L05 integrated circuit (IC) is employed as the current source for the circuit. It maintains a 5 V output voltage across R3, resulting in a current (Io) of 7.4 mA, calculated as Io = Uo/R3 = 5/680 A. However, the 78L05 also consumes around 3 mA from the central terminal. Thus, the load current cumulates to around 10 mA, which is safe for charging NiCd batteries. An LED has been added to indicate the active charging current.
Charging Current
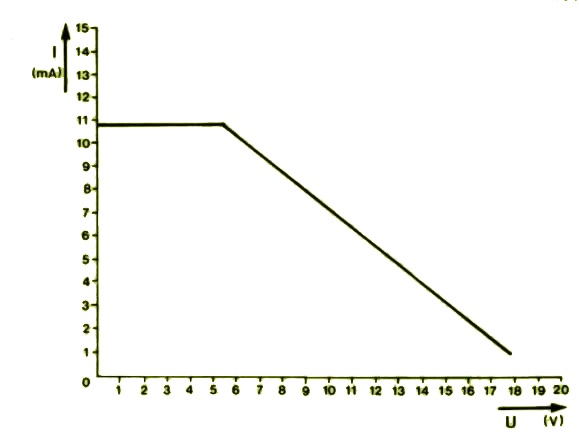
The graph plotting the charging current against the battery voltage shows that the current is not ideal, as a 12 V battery is charged with only 5 mA. This limitation is due to several factors, such as:
- A voltage drop of 5 V across the 78L05
- A further drop of 2.5 V is required by the IC
- And a 1.5 V drop caused by the LED.
Nonetheless, a 5 mA current can continuously charge a 12 V NiCd battery with a 500 mAh capacity.
Final Thoughts
In summary, this IC 555-based NiCd battery charger circuit is a simple, accurate, and effective solution for charging all NiCd batteries. By utilizing the voltage doubler feature of the 555 IC, the circuit generates a voltage higher than the nominal voltage required to charge the battery. The circuit also ensures the charging current remains safe and suitable for NiCd batteries.
Try to create this circuit, and for any query, feel free to ask in the comment section. We would love to hear from you!