Introduction
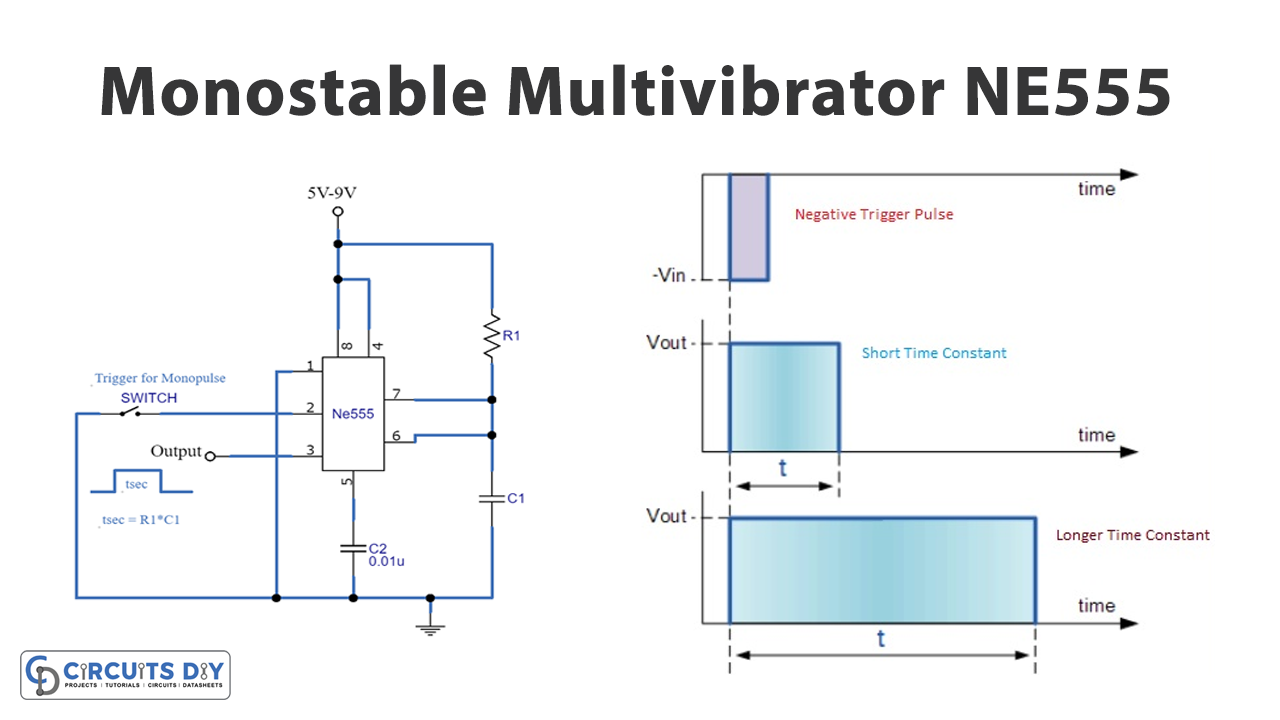
A synchronous or asynchronous sequential circuit is known as a monostable multivibrator. The circuit is frequently utilized in electronic circuits. Multivibrators have belonged to the family of oscillators known as the relaxation oscillator. These oscillators can have two states; Input high state and output low state However, 555 Timers as Monostable Multivibrators are just one stable state. This is why they are called Mono. When a negative pulse is delivered to the IC’s input trigger pin, the output generates a positive rectangular pulse. So, in this tutorial, we are going to discuss a “Monostable Multivibrator”.
‘One-shot mode’ is another term for monostable mode. It means that after the IC receives triggers, it only outputs one pulse. When the time interval has reached a specific point, the output pulse pauses and waits for the next triggered pulse. During the triggered pulse, it generated a single output pulse. In summary, we’ll use a 555 timer IC to create a monostable multivibrator.
Hardware Required
| S.no | Component | Value | Qty |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | IC | NE555 Timer | 1 |
| 2. | Push Switch | – | 1 |
| 3. | Capacitor | 0.01uF | 1 |
| 4. | Resistor & Capacitor | R1 & C1 | As your requirement |
Circuit Diagram

Working Explanation
When there is no triggering, the output is low at the output terminal of IC pin 3 and the circuit is in a stable state. If applies the negative pulse is to an IC, the trigger input goes below one-third of the applied Vcc, this resets the flip-flop of the IC and the transistor goes into the cut-off state, and the output pin 3 goes high, the capacitor starts charging through resistor Resistor. When the capacitor gets slightly greater than two-thirds of the applied voltage, the output of comparator 1 in the IC goes high and sets the flip flop, and the transistor goes into the saturation state so, the capacitor starts discharging and the output goes low.
Application and Uses
- In delay and timing circuit
- To drive pulse generator
- In regenerating old signal pulse