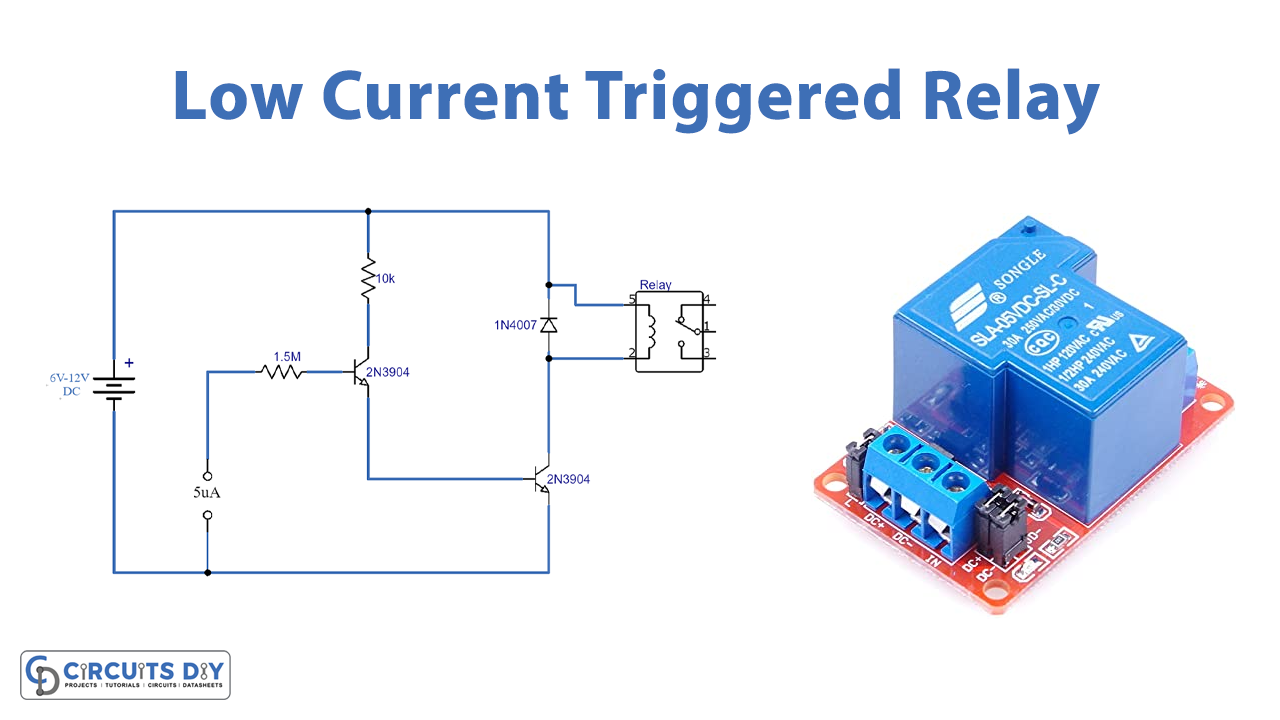
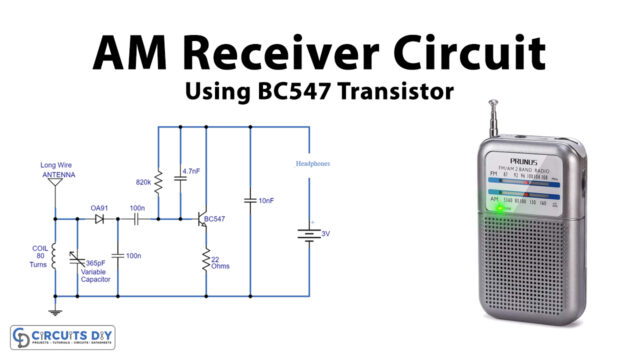
This is a project of a low current triggered relay that is used to trigger a relay switch with only 5µA current. It is done by using a bistable relay and adding a few more components to make it behave like a monostable relay. The difference between a bistable and monostable relay is that a bistable relay stays at its last state when power is turned OFF but still consumes at least 50mA trigger current whereas a monostable relay switches back to its original state when the power is turned OFF.
There is a wide range of electronic circuits and projects which have a very low current output, this circuit can be easily used with them.

Hardware Components
The following components are required to make a Triggered Relay Circuit
| S.no | Components | Value | Qty |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Transistor | 2N3904 | 2 |
| 2. | Diode | 1N4007 | 1 |
| 3. | Relay | 5V | 1 |
| 4. | Resistor | 1.5M, 10K | 1, 1 |
| 5. | Current input | 5uA | 1 |
| 6. | DC Supply | 6-12V | 1 |
2N3904 Pinout
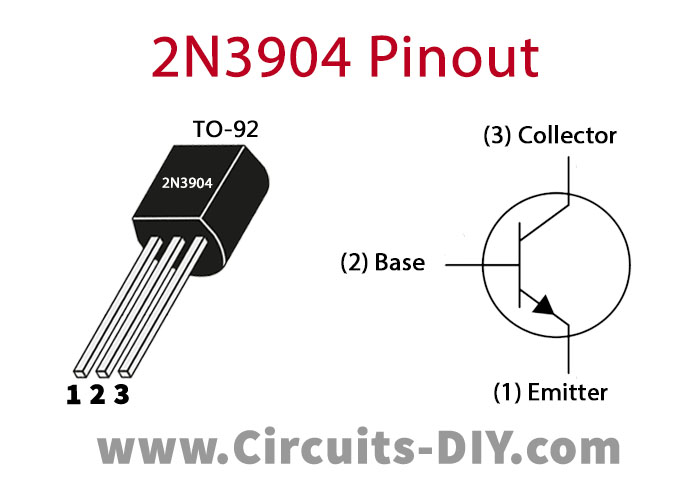
For a detailed description of pinout, dimension features, and specifications download the datasheet of 2N3904
Triggered Relay Circuit

Working Explanation
This is one of the simplest circuits, it is using only two NPN transistors, a battery, and a relay along with current limiting resistors. This circuit is powered by a 6-12V battery. The operating voltage of the relay should be the same as the supply voltage. Let’s take a look at how this circuit works,
When the power is turned on, the current input of 5µA is sent to the first transistor, the amplified output becomes the input of the second transistor. Now a large enough current is driven into the base of this NPN transistor, and the current flowing from base to emitter controls the larger relay coil current flowing through the transistor from the Collector to Emitter.
Power is applied to the coil of the relay during the switching operation of the transistor, a maximum current will flow as a result of the DC resistance of the coil. If there is no current flowing through the base of the transistor no current is passed to the coil.
Applications and Uses
This circuit is used in all battery-operated electronic devices having a low current output.