Introduction
Are you tired of constantly buying disposable batteries for your electronic devices? It’s time to make the switch to rechargeable Li-Ion batteries. And with the help of an IC 555 Li-Ion battery charger circuit, you can easily charge your batteries at home without spending on new ones. In this blog, we’ll guide you through the process of building your own Li-Ion battery charger circuit using the popular IC 555 timer.
The IC 555 is an industry-standard timer IC with many uses in different electronic applications. This circuit is robust, efficient, and easy to build, making it ideal for both hobbyists and professional electronic enthusiasts. So, let’s dive in and explore this innovative circuit and see how it can transform the way we charge our batteries.
Hardware Required
| S.no | Components | Value | Qty |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | IC | 741, NE555 | 1 |
| 2 | Capacitor | 10uF | 2 |
| 3 | Resistor | 2k7, 1k, 22k, 18, 620, 8k2 | 3, 3, 1, 1, 1, 1 |
| 4 | Transistor | BC547, 2N2907 | 1, 1 |
| 5 | Zener Diode | 2.5V | 1 |
| 7 | LED | RED | 1 |
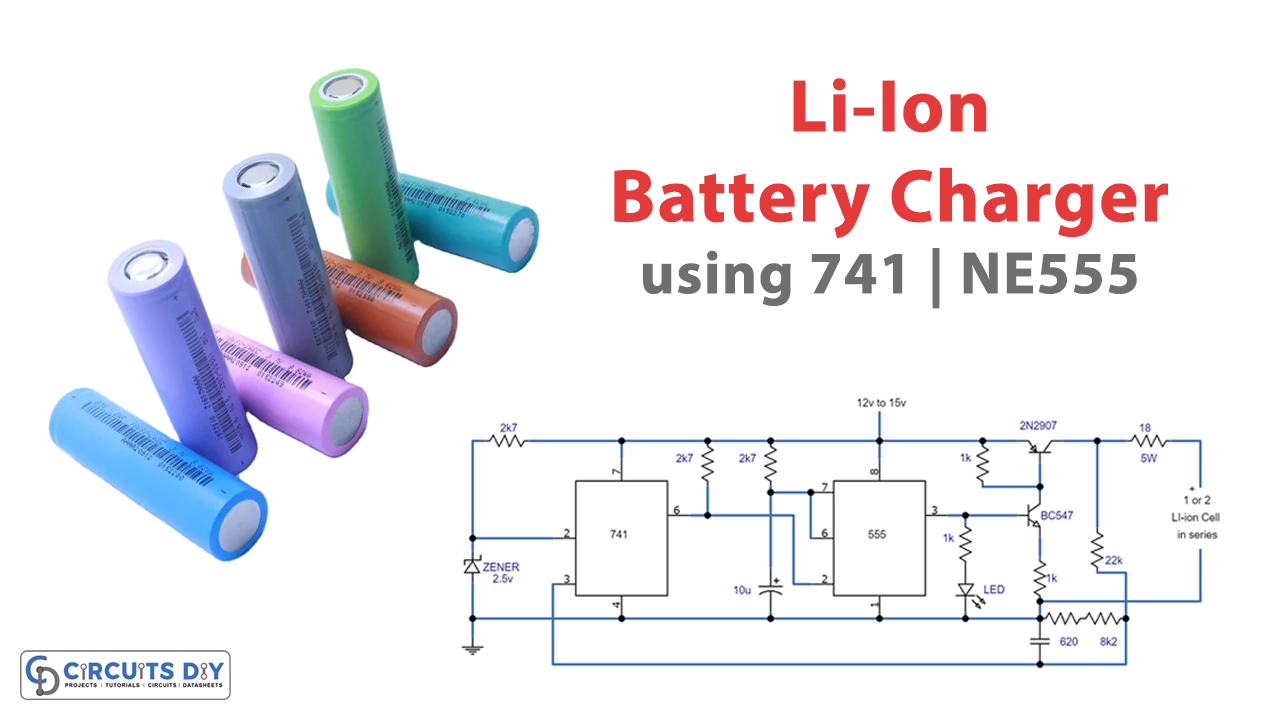
Circuit Diagram

How the Charger Circuit Works
The charger circuit operates by transmitting a brief current pulse through a series resistor and then scrutinizing the battery voltage to determine if another pulse is needed. One can change the series resistor or adjust the input voltage to adjust the current. When the battery has a low charge, the pulses are closely spaced together to maintain a somewhat constant current. Progressing towards full charge, the pulses are phased further apart, and a slowed-down LED blinking rate indicates the full charge state.
To ensure that the comparator output triggers the 555 timer when the voltage at pin 7 is below 2.5 volts, a Zener voltage reference of 2.5 volts is applied to pin 2. The 555 timer then activates two transistors, charging the batteries for approximately 30 milliseconds. After that, the battery voltage is measured and divided down by the combination of 22K, 8.2K, and 620-ohm resistors. This setup ensures that the input at pin 7 of the comparator rises slightly above 2.5 volts when the battery voltage reaches 8.2 volts, causing the circuit to stop charging.
Final Thoughts
The suggested circuit for charging Li-ion batteries using IC 555 can be employed to charge various battery types such as Ni-Cad, NiMh, or lead acid. However, to maintain the input to the comparator at 2.5 volts when the battery voltage is reached, the 8.2K and 620-ohm resistors must be adjusted to set the shut-off voltage.
It is important to avoid overcharging batteries, and testing the circuit using a large capacitor in place of the battery is recommended to ensure that it shuts off when the correct voltage is reached.
So go ahead and try it – you’ll be amazed at what you can accomplish with a few simple components and a little technical know-how.