Introduction
Looking for an FM radio circuit that is easy to build and delivers high-quality reception? You’ve come to the right place!
In this article, we will introduce you to the most straightforward and efficient FM radio circuit that even beginners can easily construct. Thanks to its unique synchronized oscillator composed of transistors, this circuit can easily synchronize with FM stations, providing an impressive reception quality. Whether you’re an electronics enthusiast or a curious beginner, this circuit is sure to amaze you with its simple yet powerful design.
Hardware Required
| S.no | Components | Value / Model | Qty |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Transistor | BF324, BC560, BC550 | 3,2,1 |
| 2 | Capacitor | 4n7, 4p7, 68p, 100p, 680p, | 2,1,1,1,1 |
| 3 | Polar Capacitor | 1uF, 4u7 | 1, 1 |
| 4 | Resistor | 18k, 1k8, 220m 22k, 47k, 1k2, 5k6, 33k. 1k | 3, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1 |
| 5 | V. Resistor | 10k | 1 |
| 6 | Inductor | – | 3 |
| 7 | V. Capacitor | 14p | 1 |
Circuit Diagram
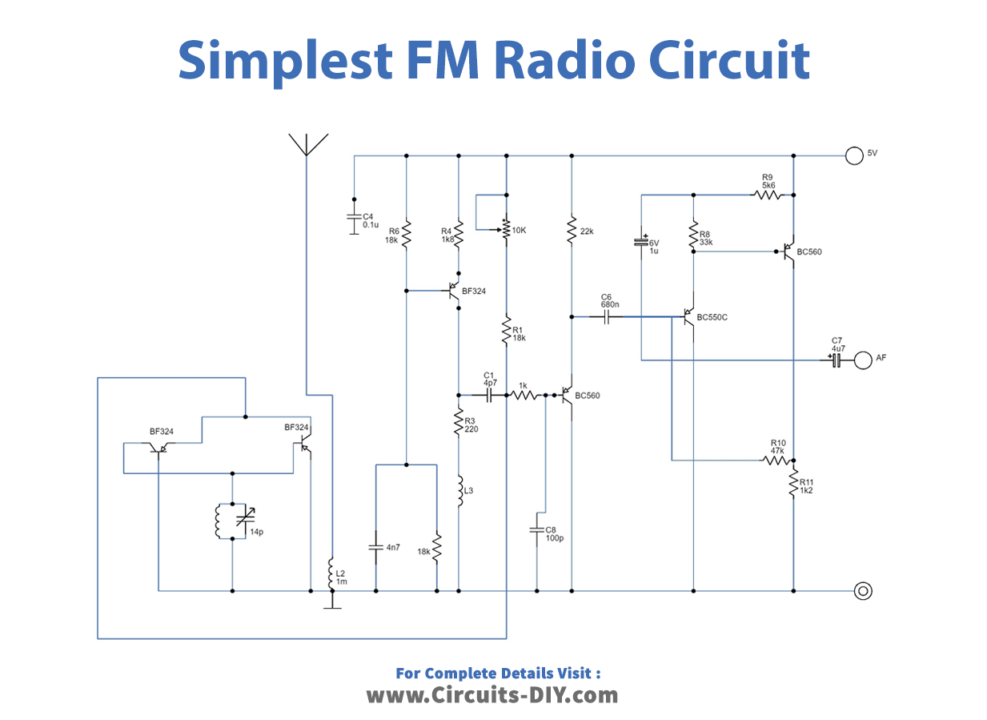
Construction of the Circuit
The winding specifications for the various coils are provided above the circuit diagram. The circuit is tuned to different stations using tuning capacitor C5, and potentiometer P1 should be adjusted to enable ideal FM reception. When combined with a loudspeaker and amplifier, such as an LM386 amplifier, this simple FM radio circuit can be made into a very sleek and compact pocket radio.
The Theory Behind the Circuit
The circuit uses a unique amplification method through transistor T1, which acts as a wideband HF preamplifier for the FM band. The oscillator is tuned using capacitor C5 to between 87 and 108 MHz, which means the frequency exhibits the same oscillations as the transmission captured by the antenna. The AF data is acquired through the oscillator, which is viewed as an inverted transmitter.
How the Circuit Works
A small modulating voltage across P1/R5 can bring about frequency modulation. If the transmission is already frequency-modulated through another method, a modulated voltage will be created around P1/R5, signifying the primary data sent. After demodulation through low-pass filtering and amplification, the demodulated AF transmission is introduced into the circuit.
Conclusion
With this super simple yet powerful FM radio circuit, you can easily tune into your favorite radio stations. The unconventional theory behind this circuit is fascinating, and building it is an exciting adventure for hobbyists and enthusiasts alike. With impressive reception quality and easy construction, this circuit is perfect for anyone looking to enjoy quality FM radio on the go. So, why not try it and embark on an exciting journey to build your own sleek and compact pocket radio!