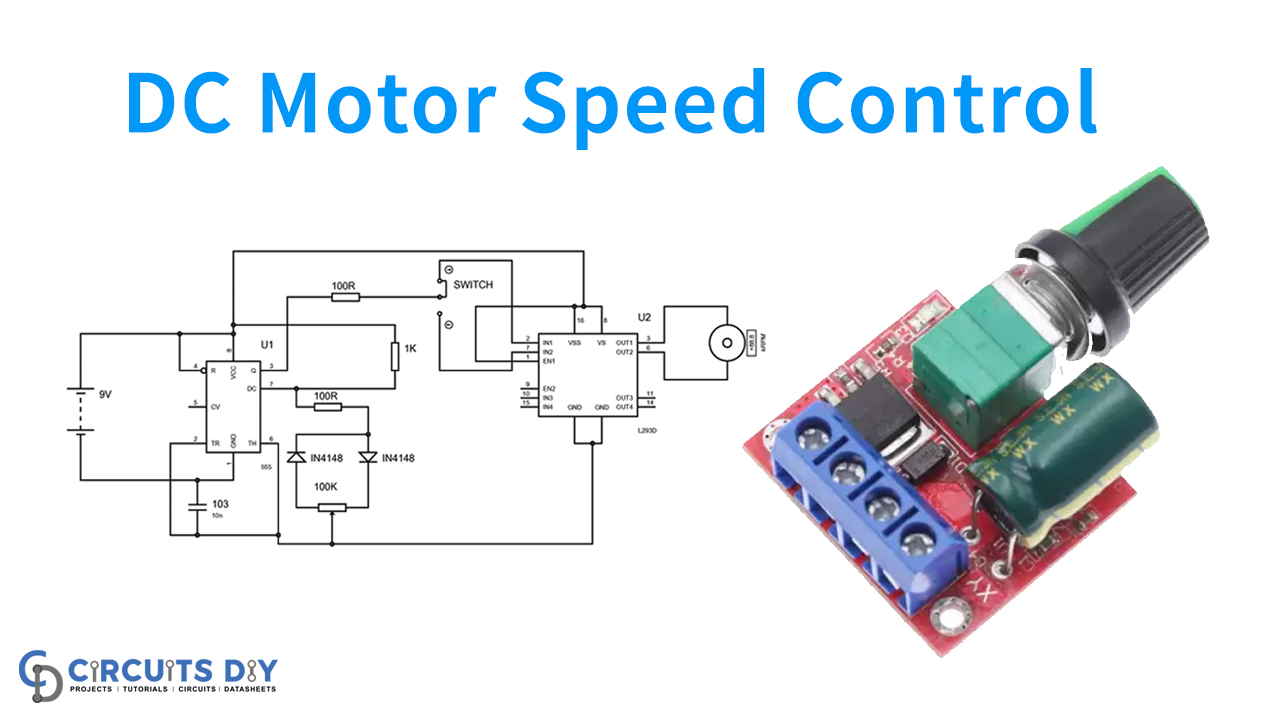
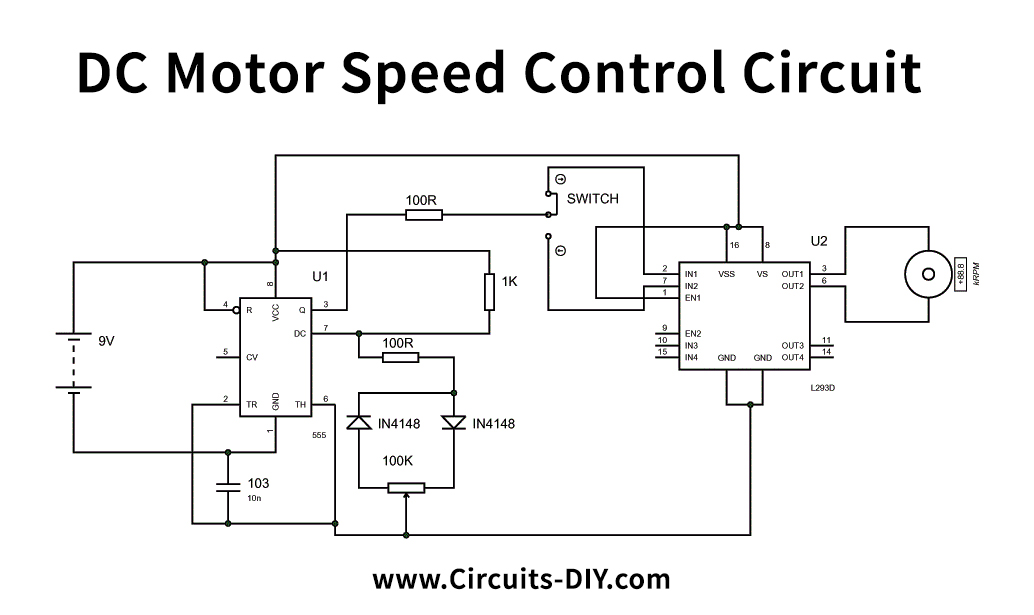
In this tutorial, we are demonstrating the project of a DC Motor Speed Control Circuit. The main feature of the DC Motor Speed CONTROL is a 555 IC-based PWM circuit, designed to obtain variable voltage over constant voltage. Here is the procedure for PWM.
Take a simple circuit, as seen in the following diagram. This circuit is easy to manufacture and requires a few low-cost components, including a power supply, DC Motor, 555 timer IC, resistors, capacitor, potentiometer, switch, and an L293D IC.

Hardware Component
The following components are required to make DC Motor Speed Control Circuit
| S.no | Component | Value | Qty |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | IC | NE555 timer | 1 |
| 2. | Capacitor | 10nF | 1 |
| 3. | Switch | – | 1 |
| 4. | Diode | IN4148 | 2 |
| 5. | potentiometer | 100K -220K | 1 |
| 6. | IC | L293D | 1 |
| 7. | Small DC motor | – | 1 |
| 8. | Power supply | 9V | 1 |
| 9. | Resistor | 1K, 100R | 1 |
NE555 IC Pinout

For a detailed description of pinout, dimension features, and specifications download the datasheet of 555 Timer
DC Motor Speed Control Circuit
Working Explanation
555 TIMER IC produces a PWM signal dependent on the potentiometer resistance ratio for power supply, with a duty ratio. The capacitor must load and unload a different set of resistors here due to the potentiometer and the diode pair. Thus, the capacitor takes a different time to charge and unload. The output is high during the loading of the capacitor and low during the unloading of the capacitor. We vary in high output, low output times, and hence in the PWM.
The timer PWM is fed to the L239D h-bridge signal pin to drive the DC generator. We get different RMS terminal voltage and rpm with the differing PWM ratio. The PWM of the timer is attached to the second signal pin to shift the directions of the rotation.
Applications and Uses
DC motors are suited to many applications – including conveyors, turntables, and other applications involving dynamic speed and constant and low-speed torque. They fit well even in complex applications for dynamic braking and reverse control, popular in many industrial types of machinery.