Introduction
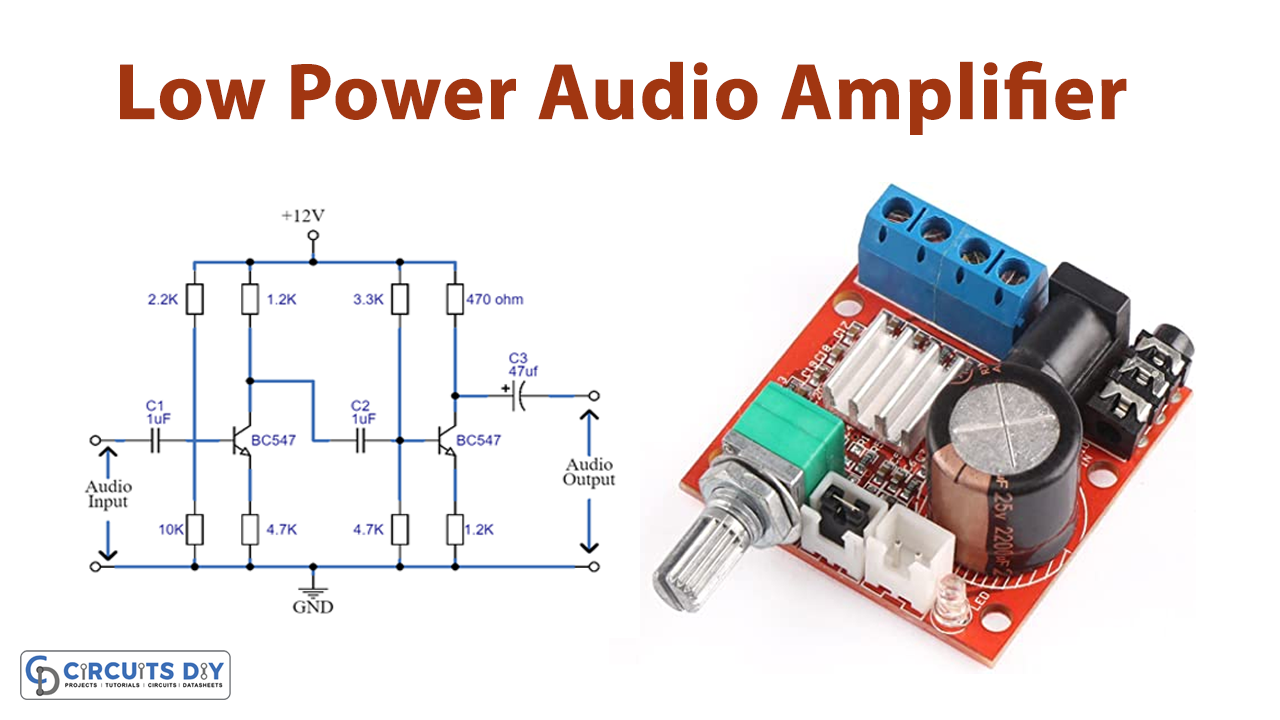
As we already knew that amplifiers are the signals that increase the voltage, or power amplifiers. thus, voltage amplifiers convert very low voltages into higher voltage while the power amplifier increases both the current and the voltage of the input signals. Our m, main focus here is to understand the low-power amplifier. Remember that amplifiers change the amplitude of the signal from lower to higher value but the frequency and shape of that signal remain the same. Low power audio amplifiers transform the low audio voltage and current into high voltage and current. To get deeper into the circuitry, in this tutorial, we are going to “Audio Amplifier-Low-power”.
The circuit uses the BC547 NPN transistor in which the collector and emitter are reversed biased when there is no voltage applied at the base. The collector and emitter get forward biased when the voltage is applied at the base of this transistor. Moreover, the maximum current flows from the collector pin are 100mA. In other words, one cannot connect any element to it that draws a current of more than 100mA

Hardware Components
The following components are required to make Low Power Audio Amplifier Circuit
| S.no | Component | Value | Qty |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Transistors | BC547 | 2 |
| 2. | Ceramic Capacitor | 1uF | 2 |
| 3. | Resistor | 4.7K, 1.2K, 2.2K , 10K, 470R, 3.3K | 2,2,1,1,1,1 |
| 4. | Electrolyte Capacitor | 47uF | 1 |
BC547 Pinout
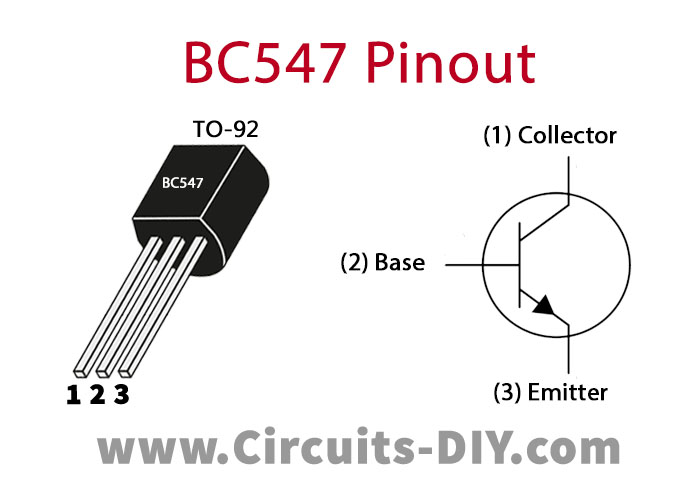
For a detailed description of pinout, dimension features, and specifications download the datasheet of BC547
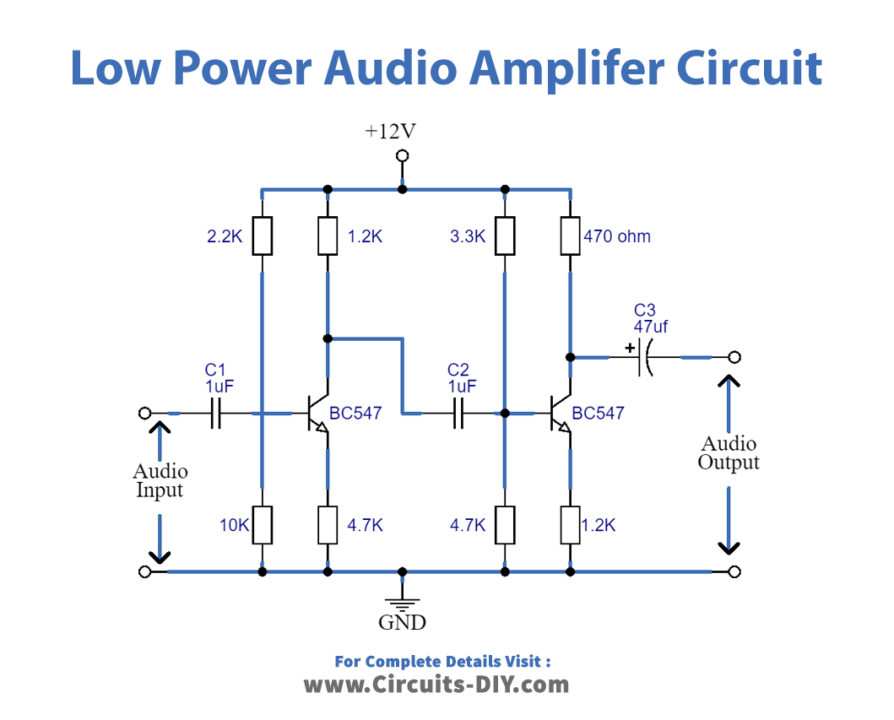
Low Power Audio Amplifier Circuit
Working Explanation
This Audio Amplifier-Low-power uses the two BC547 transistors. Since we know that amplifiers do not change the shape or frequency therefore it is necessary to use two transistors. Both the transistors are working in the same way. The first amplifier amplifies the signal and provides 180 degrees of the phase shift. As we need no phase shift, that’s why the second transistor does another phase shift of 180 degrees. Consequently, we get the phase shift of 360 degrees, which is 0 degrees in general. hence, we get the amplified output signal with zero phase shift.
Application and Uses
- Consumer electronic devices.
- Televisions, laptops.
- Headphone drivers, etc.