The use of metal clads and cores in PCB manufacturing has seen a certain uprise in the past decade. Generally, aluminum is the preferred material to be used as a clad in PCBA assembly. Mainly because of its ability to localize and direct the board thermals away from the vital components. In addition to that, the use of aluminum clads in the making of PCBs also adds to the strength and durability of the PCB board which common materials such as fiberglass and ceramic have no hope of providing. So, in today’s guide, we’ll familiarize ourselves with an introduction to aluminum clad PCB and its various kinds and applications.
What is an Aluminum Clad PCB?
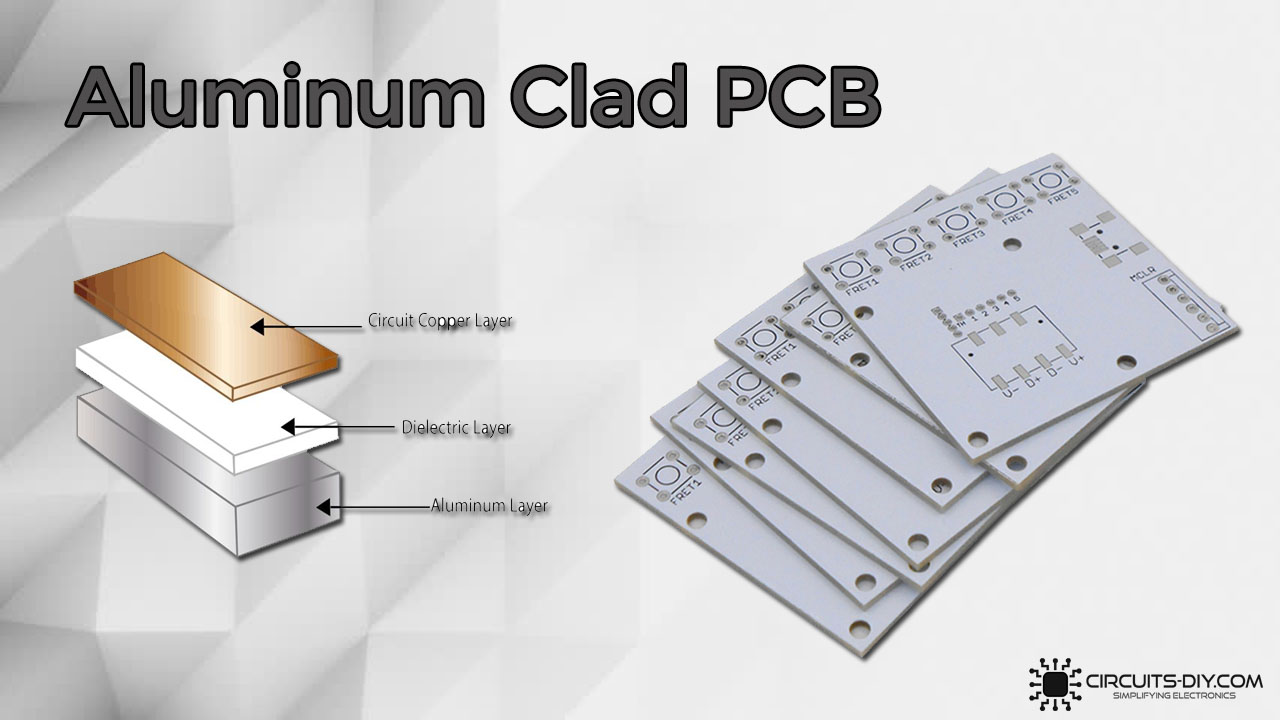
An Aluminum clad PCB contains a di-electric metal base bonded with a copper circuit layer, in order to create superior heat transfer capability, that helps to cool vital PCB components while eliminating problems connected with managing fragile ceramics. They are generally designed out of a thin layer of thermally conductive but electrically insulating dielectric material that is laminated between a metal base and a copper foil. The copper foil is etched into the desired circuit pattern and the metal base draws heat away from this circuit through the thin dielectric. Aluminum PCBs mostly function in LED and power converting electronics. The intense light produced by LEDs creates high levels of heat, which aluminum directs away from other components.

JLCPCB is the foremost PCB prototype & manufacturing company in china, providing us with the best service we have ever experienced regarding (Quality, Price Service & Time).
Structure of An Aluminum Clad PCB
At the beginning of this introduction, we’ll look at the key features that constitute the structure of an aluminum clad PCB. The general architure of an aluminum PCB is very much similar to that of any FR4 (Flame retardant) PCB. With the only difference being that that CCLs (Copper Clad Laminate) is aluminum based. Following are the four basic elements that constitute the structure of an aluminum PCB:
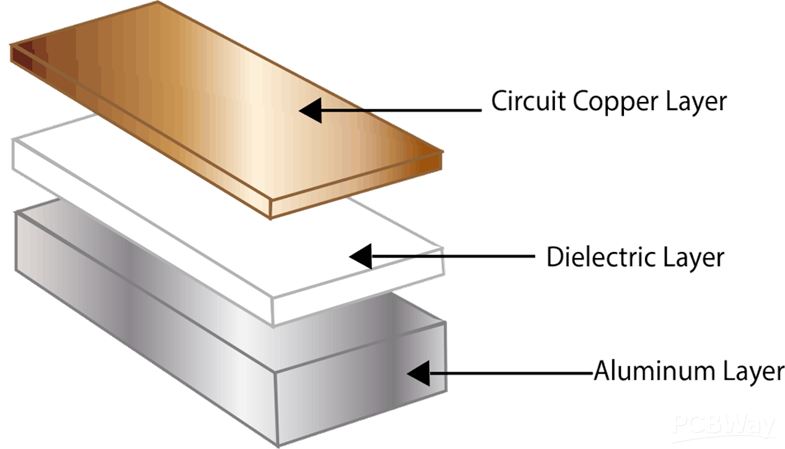
1) Copper Foil Layer
The first layer composes the circuits electrolytic copper foil, etched to form a printed circuit. This copper foil also functions as to realize the assembly and connection of the device. On comparing this with the traditional FR-4 PCB structure, with the same thickness and the same line width, the aluminum PCB substrate has a much higher current drive and tolerance.
2) Dielectric Insulating Layer
The dielectric insulating layer is the core technology of the aluminum substrate PCB. It serves the functions of bonding, insulation, and heat conduction. It is also the largest thermal barrier in the aluminum substrate insulating layer PCBs power module structure. The better the thermal conductivity of the insulating layer. The more favorable it becomes to spread the heat generated during the operation of the device and to lower the operating temperature of the device. This helps to increase the power load of the module, reduce the volume & extend the life-span.
3) Aluminum Base Layer
This layer contains the aluminum base layer. The insulating metal base layer depends on the comprehensive consideration of the thermal expansion coefficient, thermal conductivity, strength, hardness, and cost of the metal substrate.
4) Aluminum Base Membrane
The base membrane layer has a substrate made from aluminum alloy. Also, it’s quite selective and protective. Thus, keeping the surface of the aluminum from etching and scratching. Plus, it comes in two different types. above 250 degrees and the below 120 degrees base membrane.
Types Of Aluminum Clad PCB
Aluminum clad PCBs can be divided into four major types:
1) THT Aluminum PCBs
In a through hole aluminum PCB, a single layer of aluminum gets pre drilled and back-filled. Usually, the back-filling and pre-drilling happen before lamination application. Subsequently, In the end, it forms a core of multilayer fabrications. The plated through holes pass through the clearances in the aluminum to maintain electrical insulation.

2) Aluminum Flex PCB
Aluminum flex PCB offers a polyimide resin system with ceramic fillers. It features excellent electrical insulation, flexibility and of course thermal conductivity. Even though they are shown as to be flexible, the general intention of their operation is to bend and use them as per your needs but then keep them in the same position without changing. They are not suitable for applications that intend them to flex on regular basis.

3) Multilayer Aluminum PCB
Being common in high performance PSU market. Multilayer Aluminum PCBs are made from multiple layers of thermally conductive dielectrics. The multilayer PCB usually contains one or more layers of circuitry buried in the dielectric with blind vias acting as either thermal vias or signal vias.

4) Hybrid Aluminum PCB
Hybrid Aluminum PCBs constitute a Sub assembly of nonthermal materials that are process independent and then bind to the aluminum base with thermal materials. The most common construction is a 2-Layer or 4-Layer Sub-assembly made from conventional FR-4. Bonding this layer to an aluminum base with thermal dielectrics Provides superior thermal performance over a standard FR-4 product, improves rigidity, and eliminates costly heat sinks.

Applications of Aluminum Clad PCB
In this part of our introduction to Aluminum Clad PCB, we will go over some of the applications that aluminum clad PCBs have to offer:
- Aluminum PCBs have use in Communication electronic equipment such as High-frequency amplifier, filtering appliances, and transmitter circuit
- Also function in Office automation equipment such as Motor drive, etc.
- Also used in Automobile equipment such as Electronic regulator, ignition, power supply controller, etc.
- Functions in consumer electronic products such as CPU board, floppy disk drive, power supply devices, etc.