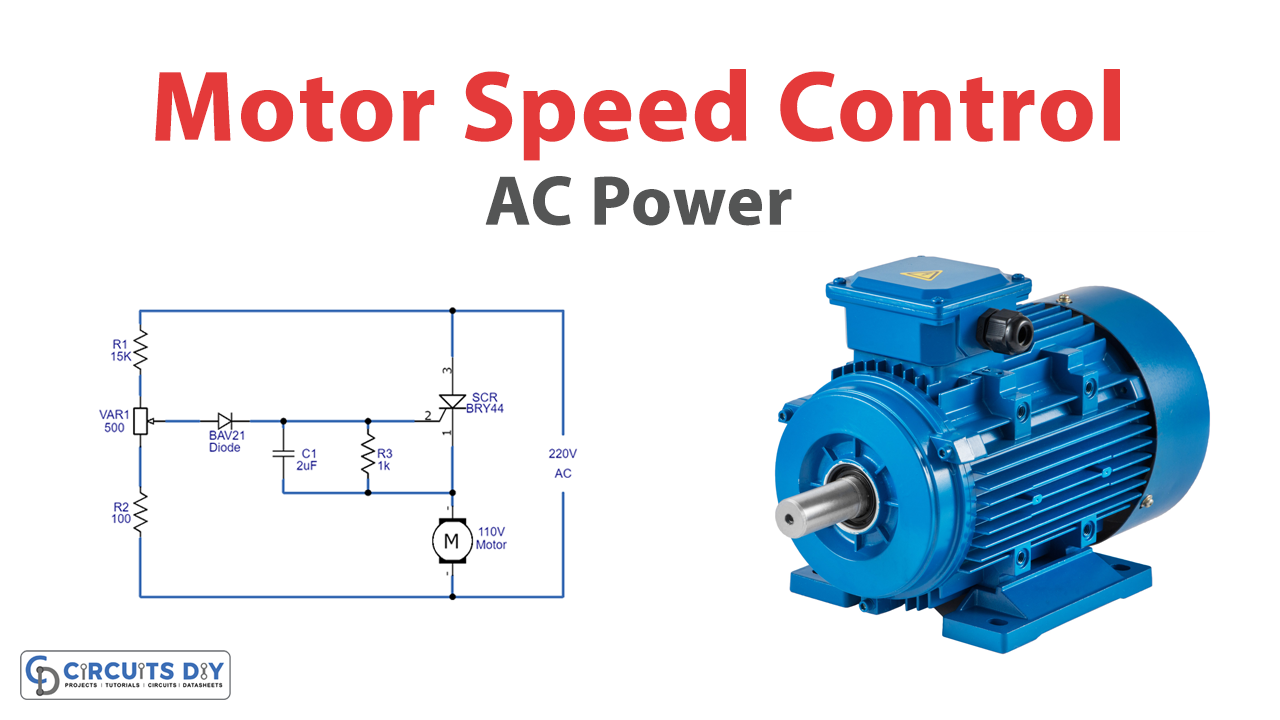
Alternating current (AC) motors are among the most widely used electric motors in several industries today. As its name implies, an AC motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. These motors offer several advantages over direct current motors. For example, they have no brushes or commutators (unlike DC motors), making them cheaper, simpler, and more reliable in producing mechanical energy. But one challenge that has remained constant with AC motors is how to control the motor speed accurately. Here we design a simple AC motor control circuit.
Hardware Required
| S.no | Components | Value | Qty |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | SCR | BRY44 | 1 |
| 2 | Capacitor | 2uF/220V | 1 |
| 3 | Diode | BAV21 | 1 |
| 4 | Resistor | 1K,100Ω | 1,1 |
| 5 | Variable Resistor | 500Ω | 1 |
| 6 | Connecting Wires | – |
Circuit Diagram
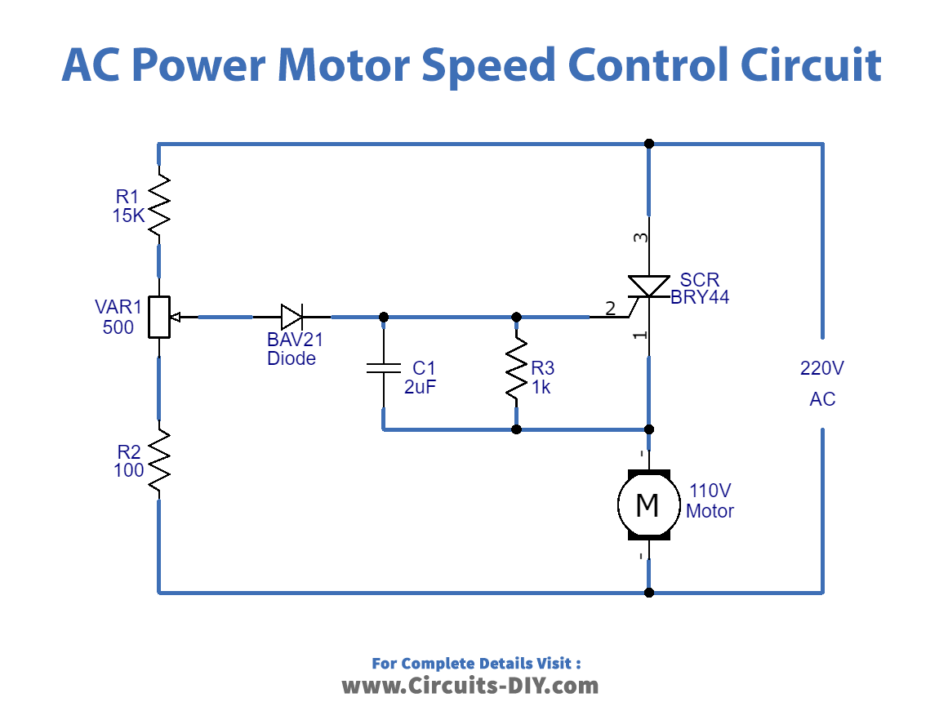
Working Explanation
TRIACs are mainly used in power control to give full wave control. This enables the voltage to be controlled between zero and full power. It provides a wider range of control in AC circuits without the need for additional components, e.g. bridge rectifiers or a second thyristor needed to achieve full wave control with thyristors. The triggering of the TRIAC is also simpler than that required by thyristors in AC circuits, and here in this circuit, it is achieved by using a simple DIAC.
Applications
Use to control the speed of AC motors.