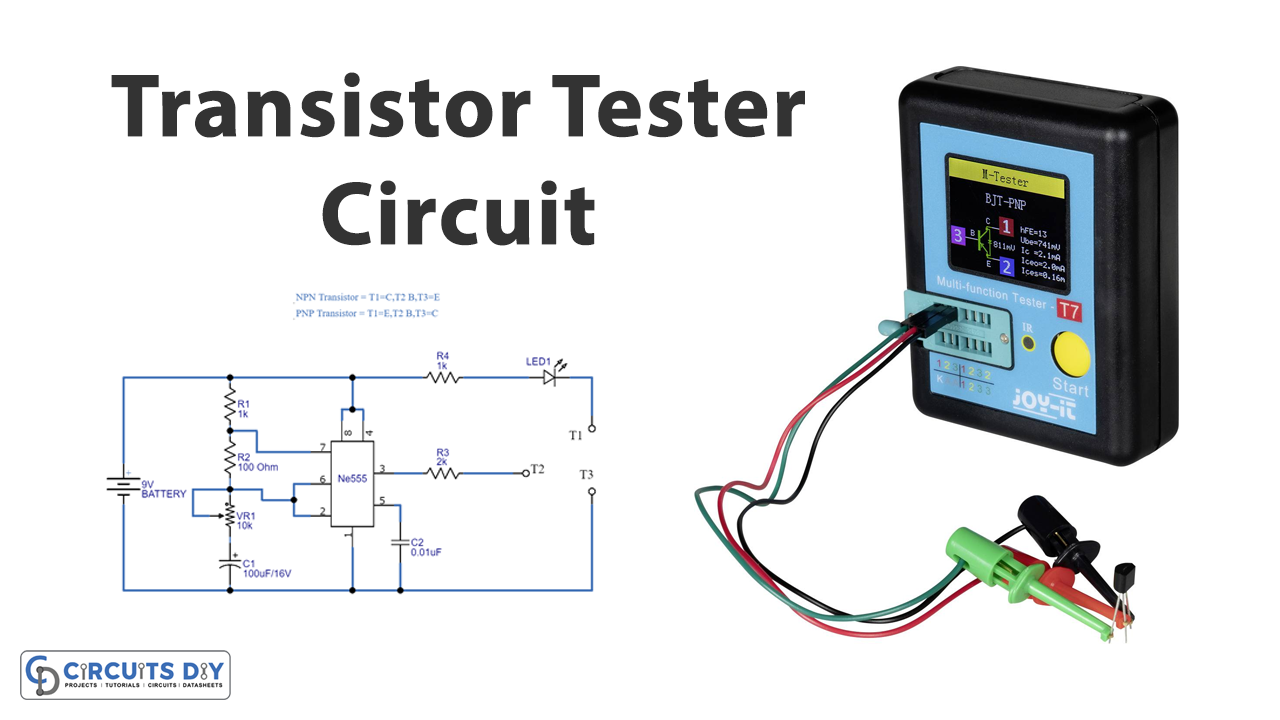
In this tutorial, we will make a “Transistor Tester Circuit Using 555 Timer”. In electronics, most circuits and prototypes are designed with transistors. While working with circuits faulty components drive us crazy, it’s quite a common scenario for electronics DIYers to run into some faults while setting up a circuit. In a good number of cases, the problem lies regarding troubles in the transistor. Therefore, the testing of the transistor is very important to avoid future inconvenience and loss to the manufacturer. For this, you have to check the transistor condition. In the same way, it is better to practice testing before implementing the transistor in circuits. A transistor tester is an instrument that is used to test the electrical behavior of a transistor.
Here we design a simple transistor tester circuit using a 555 timer to test all kinds of transistors, this schematic has one indicator LED and it will blink if the transistor works well, and stays in off condition if the transistor is open or not working. It is better to test the circuit with a Known good transistor (NPN and PNP) before testing the unknown transistor. Place the Correct pin in test points and check the transistor datasheet for the exact pin configuration.

Hardware Component
The following components are required to make Transistor Tester Circuit
| S.no | Component | Value | Qty |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Transistor | – | 1 |
| 2. | IC | NE555 Timer | 1 |
| 3. | Resistors | 1KΩ, 100Ω, 2KΩ | 2,1,1 |
| 4. | Variable Resistor | 10KΩ | 1 |
| 5. | Capacitor | 100μF, 0.01μF | 1,1 |
| 6. | Connecting Wires | – | – |
| 7. | Battery | 9V | 1 |
555 IC Pinout

For a detailed description of pinout, dimension features, and specifications download the datasheet of 555 Timer
Transistor Tester Circuit
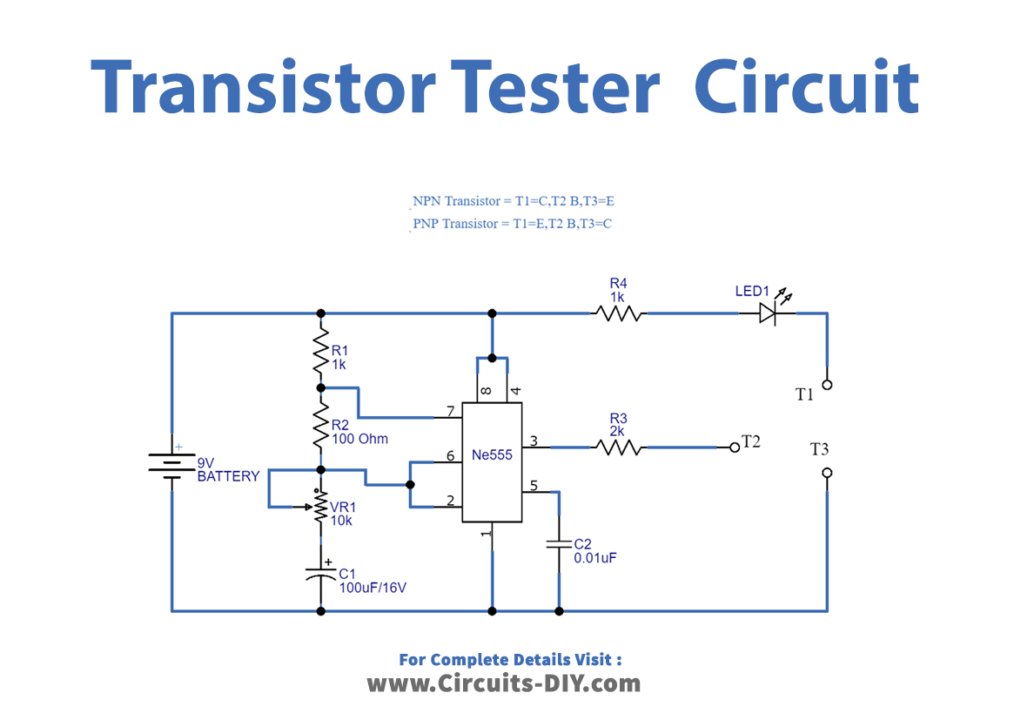
Working Explanation
In this circuit the timer function is to work as an astable multivibrator circuit and produce square pulse output (depending on the timing resistor and timing capacitor value), to provide a clock for the transistor. The output of this circuit is connected with the T2 test point, the positive supply is connected to the T1 test point through the R4 resistor and LED, Negative supply is connected to the T3 test point. Now as the clock is connected to the transistor (transistor to be tested) base, we know every transistor acts as a switch and here the NPN or PNP transistors are placed in the test point then the output pulse from the astable multivibrator drives the base of test transistor and makes the test transistor ON and OFF repeatedly. As we know that an NPN transistor responds to positive voltage only, so to turn on an NPN transistor we should give a voltage greater than 1V.
Once the positive voltage is provided at the base, the NPN transistor moves from cutoff mode to saturation mode. As for a PNP, to turn on it should be provided with a voltage less than or equal to zero. So, if the base of a PNP is connected to the ground it moves into conduction. Here the transistor is provided with a LED to drive, hence if the LED starts blinking so, then it can be considered a working transistor. And the LED stays in OFF condition if the test transistor is opened or not working.
Applications
Can be used to test transistors in electrical and electronics circuits.