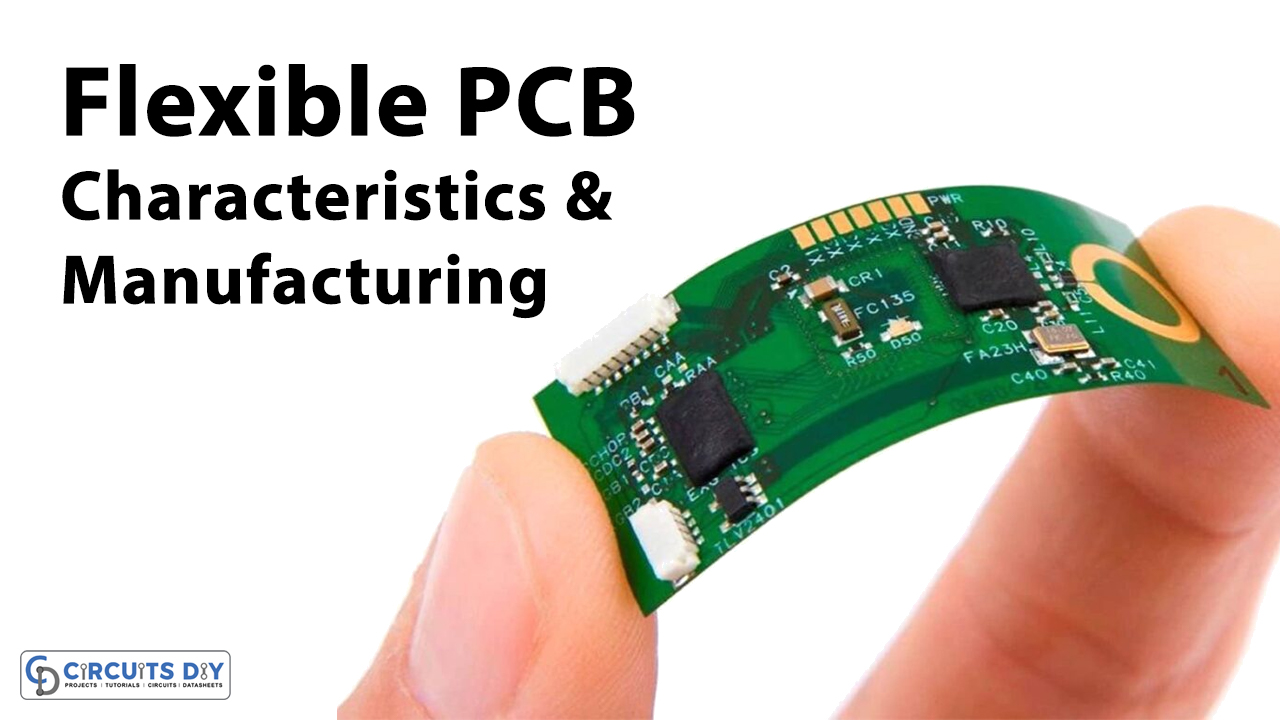
Introduction to Flexible PCB
Flexible printed circuits have another name, that is flex PCB. But, no printing photo imaging or laser imaging is used in the manufacturing process. A flexible PCB has a metallic layer usually copper bounded with a dielectric layer, that is polyamide. The circuit is protected from electrical shorting. Therefore, the dielectric material is used for non-conductive areas.
Manufacturing process of Flexible PCB:
The main thing is the polyamide, which is the base material. Since this is expensive. Therefore, try to save this by designing the circuit with the nesting technique. And, place the circuit components near each other.

Looping and Sizing
Add a slight amount of extra material. This small amount is commonly popular as a service loop. It enhances the service length and assembly of the circuit
Select the thin copper for greater flexibility. Especially when you want to make dynamic circuits
Etching and Routing
To compensate for the isotropic losses, an etching tool is necessary to use. And, Then there would be routing of the conductors. And, it modifies the folding and bending
Ground planes and Sizing
Ground areas should be allocated. And, then you need to reduce the size and weight of the circuit board. So, build holes as tiny as possible. As technology is evolving the size is decreasing day by day. Yet, the designers have capable to make 25 micrometers of small holes
Filleting and Button Plating
To make a flexible circuit, the pads need filtering. It is done by multiplying the area of pads and then distributing stress among them.
Button plating creates a plated through-hole. And, it is appropriate to make reliable solder joints
Adhesive-backed films
The adhesive-backed film is used for overcoating. Because it contains balanced rare material. Therefore, mostly used in dynamic circuits.
Overcoating
If you want to save cash, it is recommended to use screen printable liquid overcoats. However, there is an advanced technique of overcoming, that is an image. The important objective of the cover layer is to act as a cover mask. And, secure the printed circuits from any damage. Also, protects the circuit from external electrification.
Characteristics:
- Less weight and space: In maximum cases, flexible circuits significantly have lower weight and size
- Higher Current capacity: Flexible PCBs can have a higher current capacity.
- More reliable: Because of their unique design characteristics, flex PCBs are more reliable. However, they are more vulnerable since they can be torn easily
- Thermal management: Flexible PCBs have higher heat dissipation properties. However, it can manage this thermal dissipation better than its rigid counterparts.
- Cost Efficiency: The cost of flexible PCBs is much higher than the rigid ones. However, flexible wiring and installation cost are nominal. But, additional tooling makes it more expensive. Therefore, the price is high.
- Eliminate connectors: The flex PCBs have reduced the number of terminals and soldering joints. The conductor is positioned near-neutral surfaces.
- High speed: Since the components are near to each other. Results, in high-speed.
- Signal Line: Signal lines get reduced without lessening the terminal size