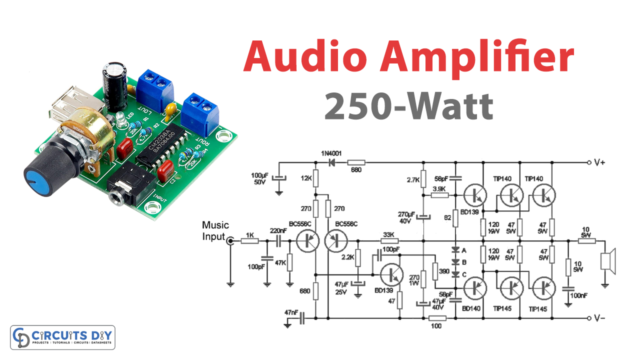
Introduction
If you hear music, you must also be familiar with its instruments. The bass guitar is a well-liked instrument. Bass lines, also known as low musical tones, are played on the bass guitar in many musical genres, including rock, pop, country, and many others. So, in this Tutorial, we are going to make a “Bass guitar super bridge amplifier of 200 watts”.
The circuit is cleverly designed with a 200-watt power output in a super bridge model to help you get a high-quality circuit for a reasonable price.
Hardware Required
| S.no | Component | Value | QTy |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | TDA2005 | – | 1 |
| 2 | Resistor Different Values | – | 34 |
| 3 | Capacitor Different Values | – | 16 |
| 4 | Speaker | – | 1 |
| 5 | Transistor | MPSA06, MPSA56, BC182, BC212, MJ3001, MJ2501 | 4, 2, 3, 1, 2, 2 |
| 6 | Diode & Zener Diode | 1N4148 | 2,2 |
| 7 | Inductor | – | 1 |
Circuit Diagram
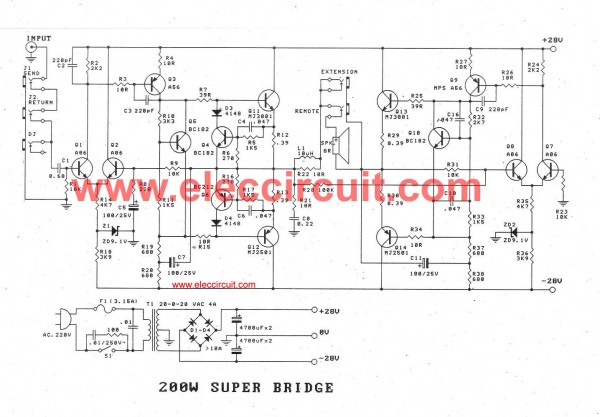
Working Explanation
In this bass guitar super bridge amplifier of 200 watts, firstly, we need a voltage supply of 28V, which is made up of the transformer T1 and lowers AC voltage of 220 volts to 20 volts, 0 volts, and 20 volts. If you have a mono amplifier, the used transformer should be able to supply a current of no less than 4 amps and no less than 8 amps in a stereo amplifier system. A parallel circuit filter is created using two capacitors with a total capacity of 4700 microfarads and four diodes, D1 through D4. To replace them, pick a 1,00 uF/35V capacitor. This power supply’s output voltage is equal to both the positive and negative 28 volts at 4 amp. At a load of 4 ohms, the output power will be less than 200 watts.
The differential amplifier Q1’s input jack, send jack, and return jack all receive the signal. As it travels to the collector and through R3 to the base of Q3’s transistor driver circuit, the signal is amplified. To drive the power transistors Q11 and Q12, the outcome at collector pin Q3 will pass two resistors R7 and R16. The transistors’ output bias current is set in a reasonable range by Q5.
Two Q4 and Q5 protect the power transistors from having an excessively high circuit. which could happen if an output short circuit occurs. We have output signal detectors for resistors R12 and R13. A high enough voltage will be across if some current exceeds the value set, making Q4 and Q6 functional. Q4 and Q6 will act as short circuits to short the voltage entering the bases of Q11 and Q12 until the output current decreases and lower in a secure manner.
The output signal enters the loudspeaker through coil L1 and then passes through R20’s inverting input as described above at the beginning. The other signal will also be entered at the same time by R9 into the inverting Q2. The value of R9, R8, and C5 determines the circuit’s growth rate.
Now, all the other circuits function in the same way as the first circuit.
Application Uses
- This circuit is used in bass guitar the main purpose is to keep a steady rhythm.