Introduction
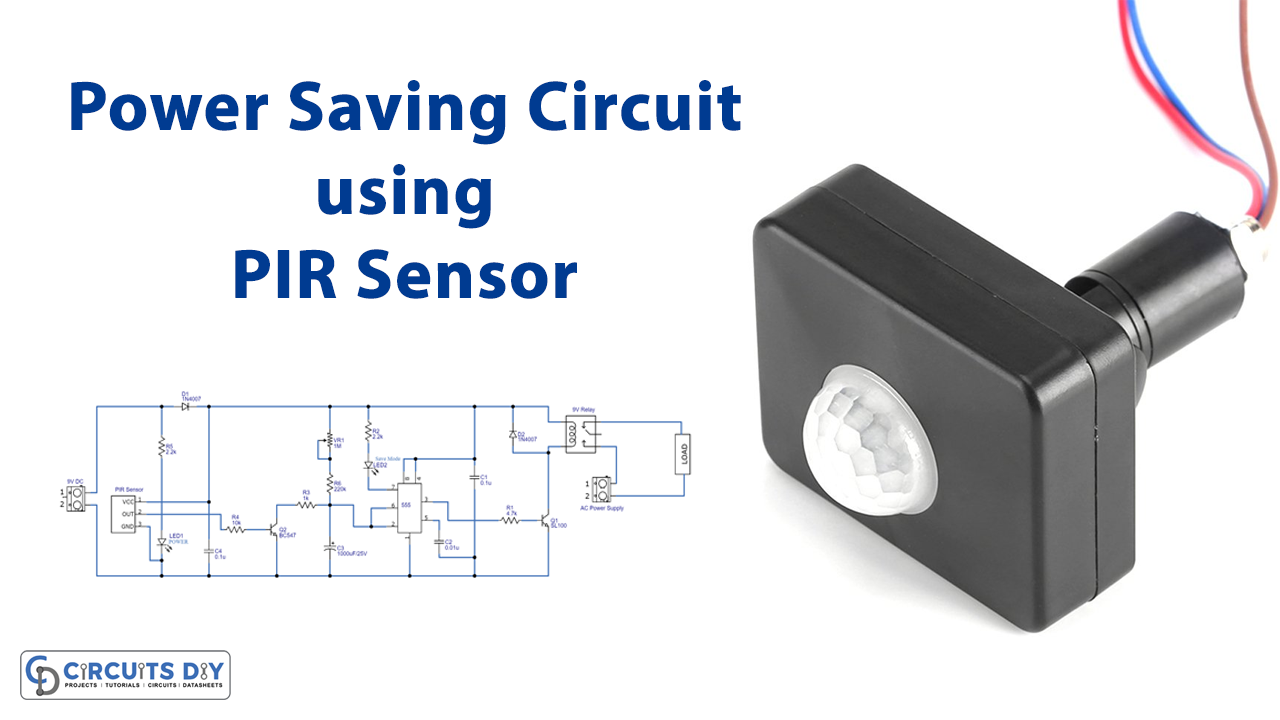
A power saver is a device that connects to a power socket. Simply maintaining the circuit will minimize your power consumption. Power saver circuits can be made in different ways. In this tutorial, we are going to make a “Power saver circuit using a PIR sensor”. The PIR The sensor has two slots in it. When there is no movement around, both the slots have the same readings. When any warm body or human is around, it inspects the heat and detects the movement. This causes a differential change between the two slots. And, output load starts its work.

Hardware Components
The following components are required to make the Power Saver Circuit
| S.no | Component | Value | Qty |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | IC | NE555 Timer | 1 |
| 2. | Transistor | BC547, SL100 | 1 |
| 3. | Connector | 3-Pin, 2-Pin | 1 |
| 4. | Relay | 9v | 1 |
| 5. | Diode | 1N4007 | 2 |
| 6. | Load Fan | – | 1 |
| 7. | Potentiometer | 1MΩ | 1 |
| 8. | Capacitor | 1000uF | 1 |
| 9. | Ceramic Capacitor | 0.1uF | 3 |
| 10. | Resistor | 1KΩ, 2.2KΩ, 4.7KΩ, 10KΩ, 220KΩ | 1,2,1,1,1 |
NE555 IC Pinout

For a detailed description of pinout, dimension features, and specifications download the datasheet of 555 Timer
Power Saver Circuit
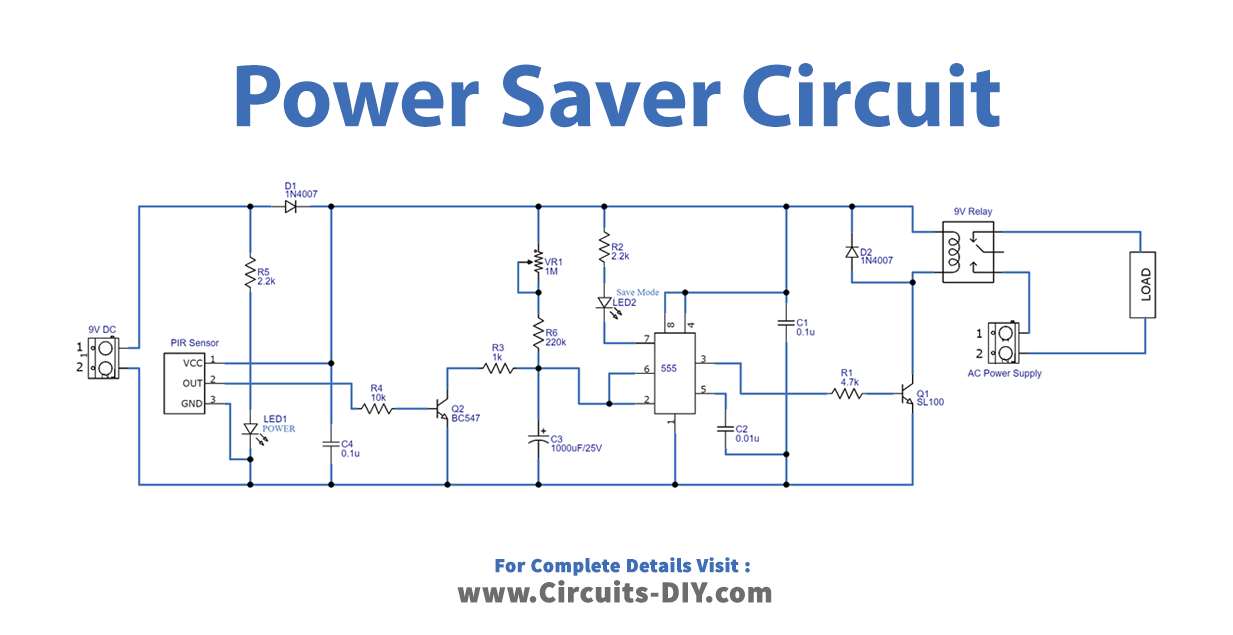
Working Explanation
The timer IC555 and the PIR sensor are the main components of this Power saver circuit. The output of the PIR sensor is supplied directly into the base of the transistor BC547, and the collector terminal of the transistor is linked to the threshold and trigger pins of the IC555 through a timing resistor and capacitor.
Through the potentiometer, we may change the sensitivity level and so the output pulse duration. The LED2 wired to the discharge pin indicates that the circuit is in saving mode. The switching transistor SL100 drives the output to the relay. The load is controlled by a 9-volt relay in this circuit.
.It is the PIR sensor that triggers this circuit and activates the relay through the timer IC output. Hence, When a person leaves the room, this circuit turns off the load device.
Application and Uses
- Home automation systems.
- In street light circuits.
- And, anywhere to save the power