Typically, LEDs are regarded as DC (direct current) devices since they run on just a few volts. This is entirely fine in low-power applications with a limited number of LEDs. However, in other applications, DC drive suffers from distance losses,
Contrarily, AC will function better over a greater distance, which is why it is the technology used to supply electricity to homes and companies worldwide. And therefore, we have decided to build an “AC-Powered 230V LED Circuit” in this tutorial.
This circuit requires essential electronic components and a little understanding of electronic circuits. Furthermore, because numerous LEDs can be connected in series, AC-powered LED technology can be defined as scalable.
Hardware Required
| S.no | Component | Value | Qty |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Diode | 1N4007 | 4 |
| 2. | Capacitor | 0.47uF, 47uF | 1, 1 |
| 3. | Zener Diode | 16V | 1 |
| 4. | LED | – | 5 |
| 5. | Resistor | 470K, 120R | 1, 2 |
| 6. | Power Supply | – | 1 |
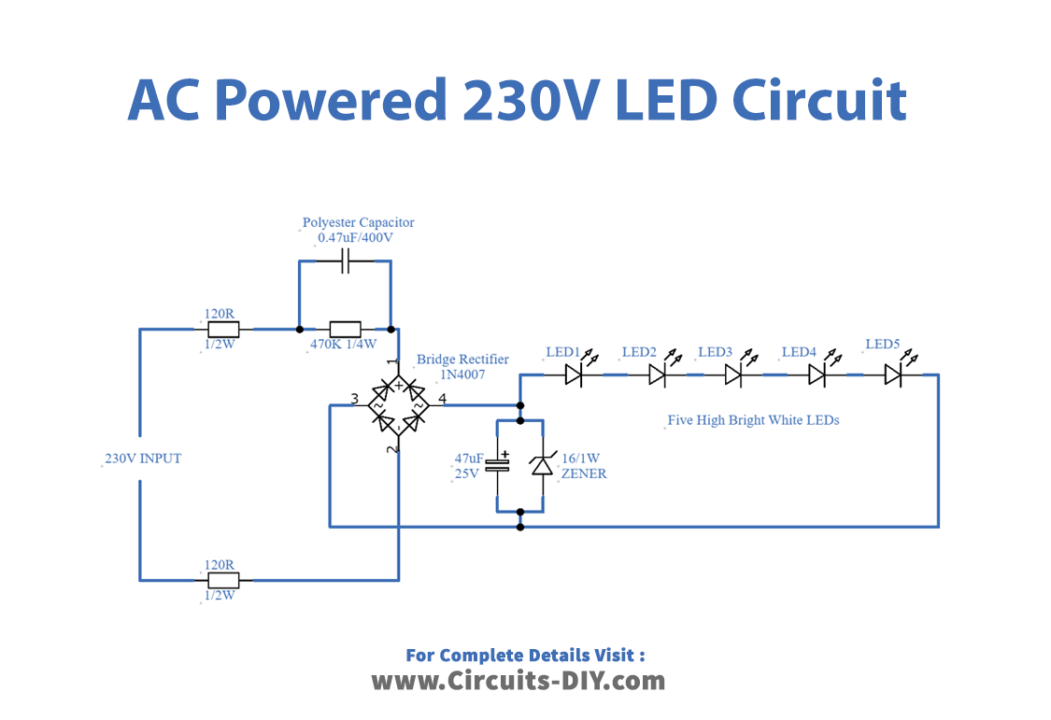
Circuit Diagram
Working Explanation
In this circuit, the AC power supply is stepped down using a polyester capacitor of 0.47F / 400V, a resistor, and a bridge rectifier to light up some LEDs without the step-down transformer. These components provide a barrier that causes the AC mains to be decreased to a lower level and transformed into a DC supply. A 47F/25V electrolytic capacitor filters the DC output at the bridge rectifier’s output while a Zener diode regulates it. The rectifier circuit powers five white LEDs, all are connected in series.
When the power supply is given to this circuit, the polyester capacitor and resistor act as a barrier against the AC mains, reducing the voltage to a lower level. The rectifier bridge then converts the AC supply into DC. The filter capacitor, Zener diode, and filter capacitor then regulate the DC output before supplying the LED array with DC power.
Application and Uses
- Power indicator circuits
- Lightning systems
- Streetlights, etc