Introduction
The power supply is the basic electronic circuit, used in every other electronic device and therefore we have seen that many students learn electronics with the first understanding of power supply circuits. The power supply converts the AC power. However, there are some circuits and devices that need a dual power supply. For example, some of the operational amplifier circuits need a dual supply because the op-amps can work with both polarities. In the same vein, DC motors need the positive and negative supply t to rotate in clockwise and anti-clockwise directions. So, n this tutorial, we are going to make a “Dual Power Supply circuit”
Hardware Required
| S.no | Component | Value | Qty |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Step Down Transformer | – | 1 |
| 2. | Diode | 1N4007 | 1 |
| 3. | IC | LM7805 | 2 |
| 4. | Capacitor | 100uf, 10uF, 0.1uF | 2, 2, 2 |
| 5. | 2-Pin Connector | – | 1 |
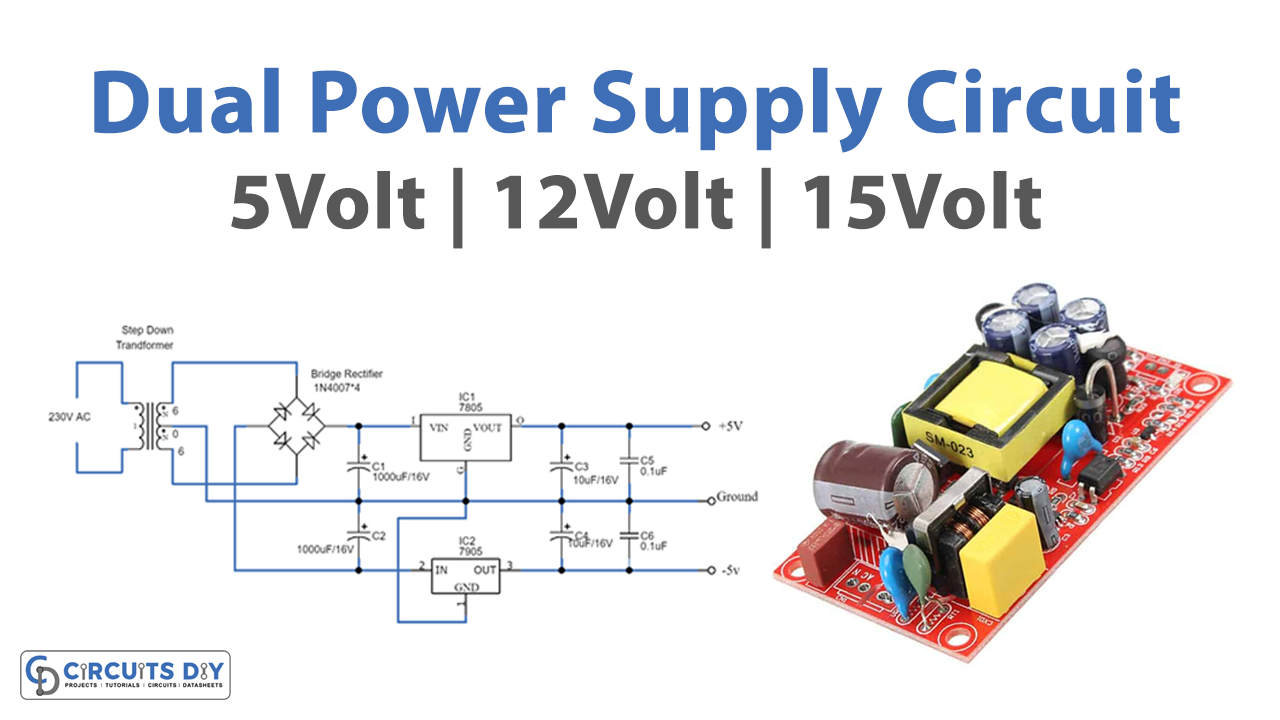
Circuit Diagram
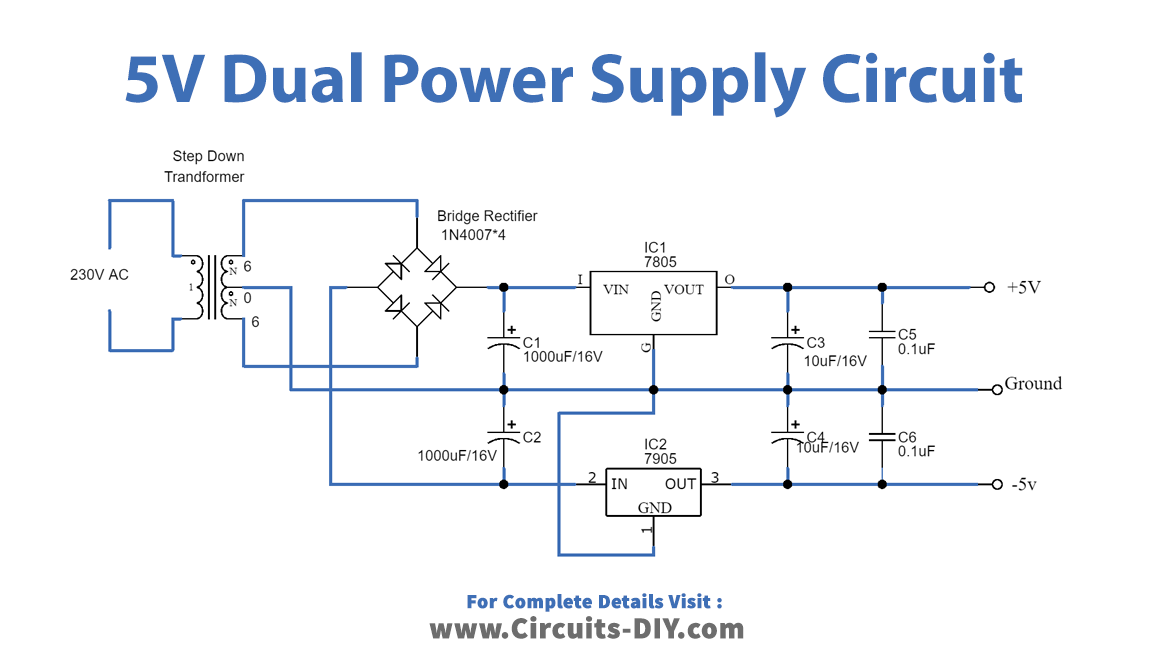
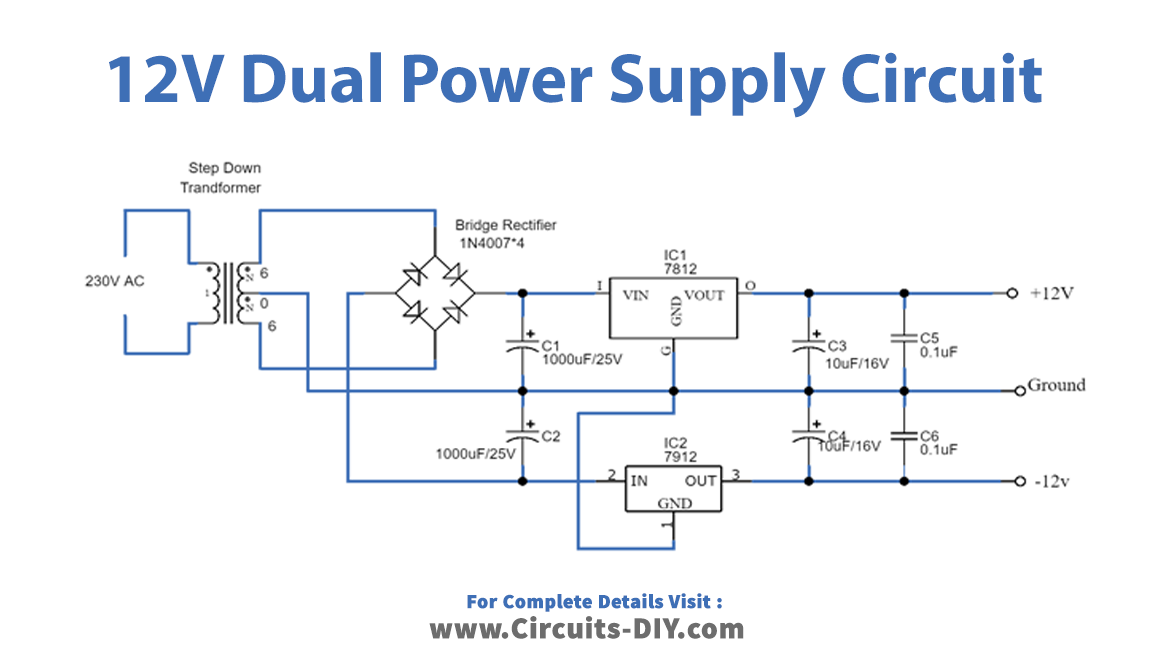
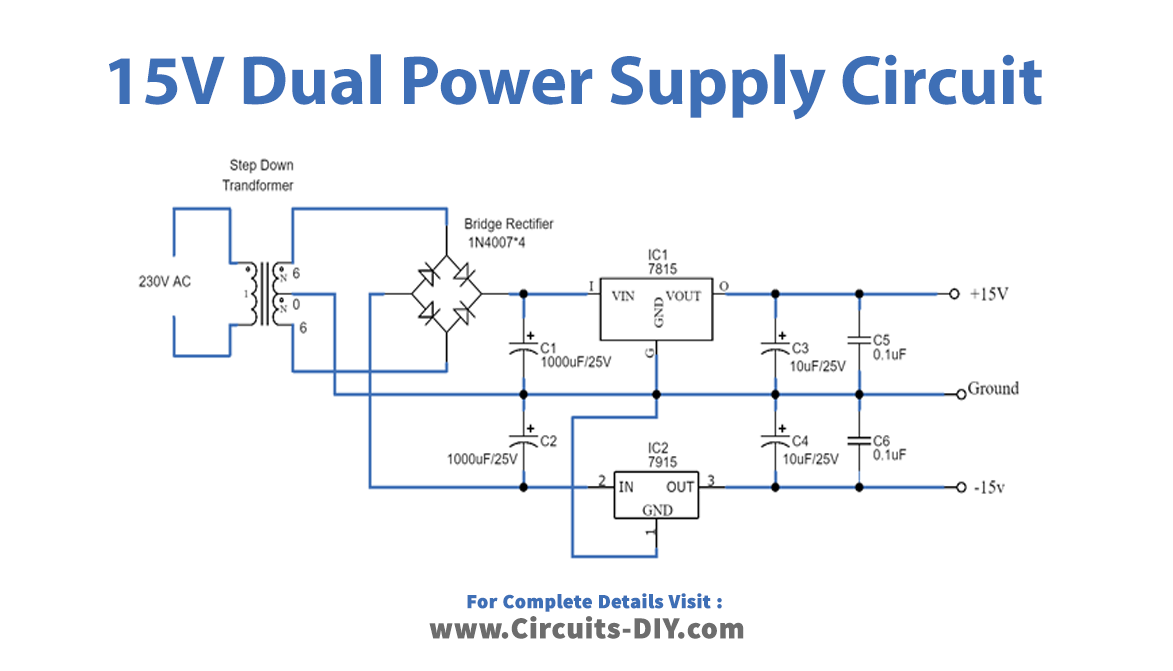
Working Explanation
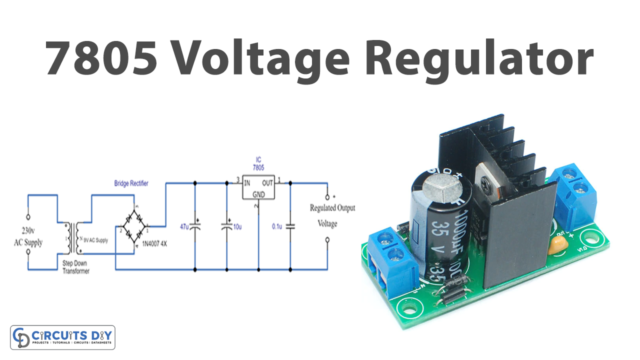
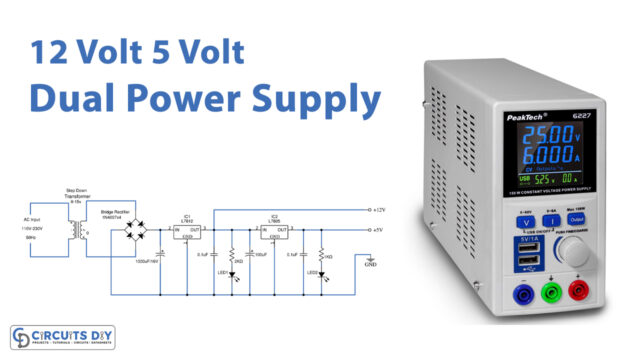
Here there are three circuits available. The only;y difference is the output voltage happens because of the different regulator ICs used in every circuit. In every circuit 78XX, IC is used to get a positive supply and we use 79XX for a negative supply. No, we will understand all three circuits through one circuit. For example, take the first one, to make a 5V Dual power Supply circuit firstly, we give the 20V-0-20, coming from the transformer to the full-bridge rectifier circuit, that we have made with the help of diodes. The rectifier converts the AC into DC but it has the DC ripples in it. These DC ripples are filtered by the capacitors C1 and C2 attached to the circuit. Now, this voltage is provided to two different regulators ICs. IC L7805 gives the positive DC voltage, while IC L7905 provides the negative DC voltage. The voltages get filtered by the capacitors wired in this circuit and we get the dual supply at the output load.
Application and Uses
- Operational amplifiers.
- DC motors.
- Negative supply of RAMs, etc