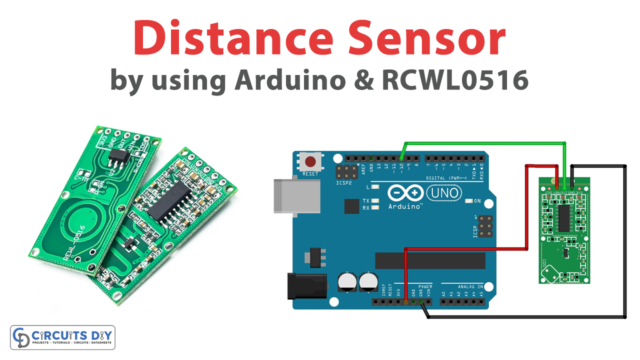
An Overview of the IC
A hall-effect sensor is an IC that is used for measuring the speed of rotating assemblies where a magnet alternately makes and breaks magnetic contact with the sensor as the assembly rotates. And therefore, We can also use them for applications like position sensing and detecting, the magnetic field created by current flow in a wire, etc.

Hardware Overview
The integrated circuitry features low noise output, which makes it unnecessary to handle external filtering. It also includes thin film resistors which give increased temperature stability and accuracy. This sensor has a ground and +5V supply with a single digital output which goes low when a magnetic field is detected.
Working
When there is no magnetic field present, the output of the sensor stands at approximately 50% of Vcc. So, with 5V power, the output will be about 2.5V. When a magnet is there, the voltage rises or falls depending on whether the south or north pole of the magnet is coming near. If we place a south pole of a magnet near the front of the sensor, the output voltage will linearly slope up towards VCC to a maximum of 4.2V. If we place a north pole of a magnet near the front of the sensor, the voltage will linearly ramp down towards the ground to a minimum of 0.86V. Hence, the amount of voltage that increases or decreases depends on the magnetic strength of the field.
Features and Specifications of 49E Hall Effect IC
Features
- Miniature Construction
- Power Consumption of 3.5mA at VCC=5V for
- Energy Efficiency
- Single Current Sourcing Output
- Linear Output for Circuit Design Flexibility
- Low Noise Output Virtually Eliminates the Need for Filtering
- A Stable and Accurate Output
- Temperature Range of -40oC to 85oC
- Responds to Either Positive or Negative Gauss
Specification
| Operating Ratings | VCC Range | 2.3 – 10V |
| Output | No magnetic field detected | 1/2 Vcc (typ) |
| Magnetic field detected – South pole max gauss | 4.2V (Vcc = 5V) | |
| Magnetic field detected – North pole max gauss | 1.0V (Vcc = 5V) | |
| Sensitivity | 1.9mV/GS (± 0.2mV/GS) | |
| Maximum Gauss | ±1200 GS | |
| Power consumption | Varies with VCC | 5mA @ 3.3V, 7.8mA @ 5V |
Pinouts of an IC
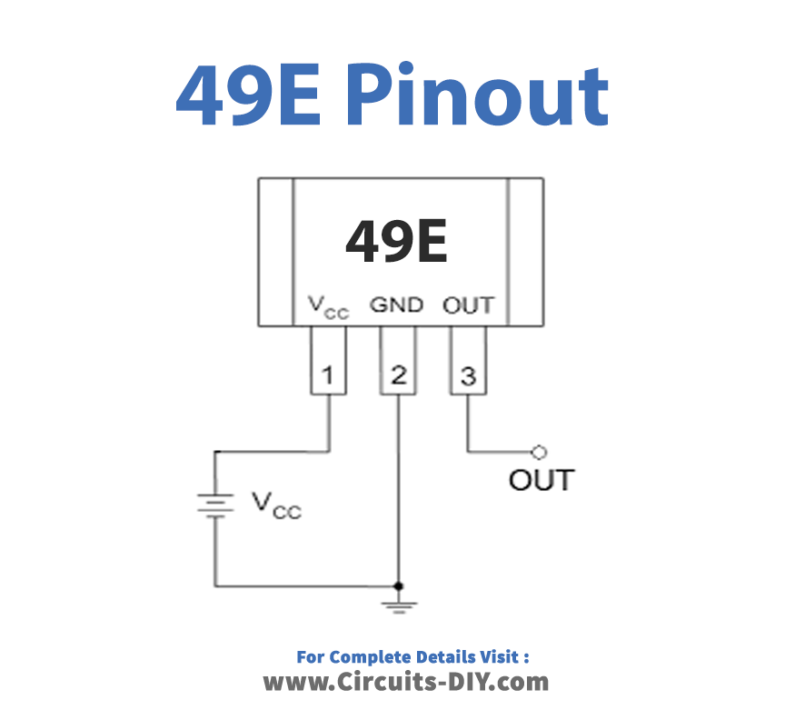
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
| 1 | Vcc | Supply Pin (typically requires 5V) |
| 2 | GND | The ground needs to be connected to the system’s ground |
| 3 | OUT | The Output of the IC |
Applications
Current Sensing
There are many interests to use hall IC for current measurement. For example, the measurement becomes more accurate because the hall sensor does not have contact with the current-carrying conductor wire. Secondly, we can use this for measuring both AC and DC. The hall sensor can measure high current with a small size device.
Motor Control
A Hall Effect Sensor is an extensively used sensor that provides rotor position feedback to a motor controller. We require a sensor to give feedback to the motor control system showing when the rotor has attained the desired position.
Position Sensing
The hall sensor can detect a magnetic field and gives output as an analog signal that is proportional to its magnitude. It converted the output of the Hall sensor to a digital signal through a comparator and then used as the rotor position signal of the brushless motor.