In this tutorial, we are demonstrating a project of a 3V FM transmitter circuit that is made of two transistors. The circuit diagram and the parts list needed to develop a 3V FM Transmitter are given in this tutorial. This FM transmitter is the least complex and most fundamental transmitter to manufacture and has a valuable transmitting range.
It is one of the best transmitter circuits in spite of its limited segment count and 3V working voltage. It will effectively enter more than three stories of a high rise and go more than 300 meters outdoors.

Hardware Components
The following components are required to make FM Transmitter Circuit
| S.no | Components | Value | Qty |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Transistors | BC547 | 2 |
| 2 | Electret microphone | – | 1 |
| 3 | Coil | 5 turns | 1 |
| 4 | Aerial Wire | 165cm | 1 |
| 5 | Variable capacitor | 6-45 pF | 1 |
| 6 | Resistor | 22K, 10K, 1M, 47K, 470 | 1 |
| 7 | Ceramic Capacitor | 22nF,27pF, 5.6pF, 1nF, 100nF | 2, 1, 1, 1, 1 |
| 8 | Battery | 3-5V | 2 |
BC547 Pinout
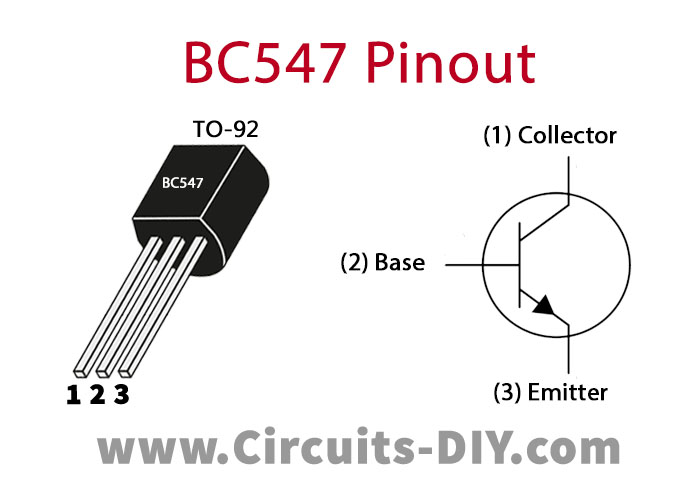
For a detailed description of pinout, dimension features, and specifications download the datasheet of BC547
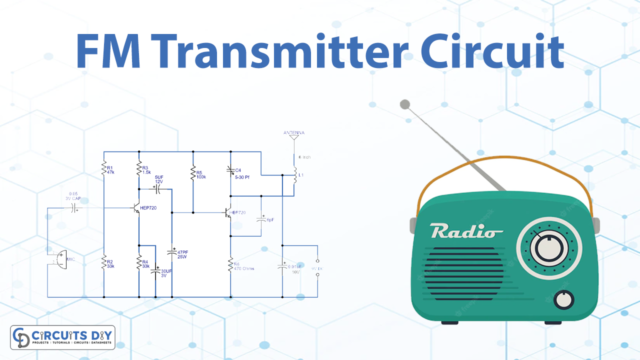
FM Transmitter Circuit
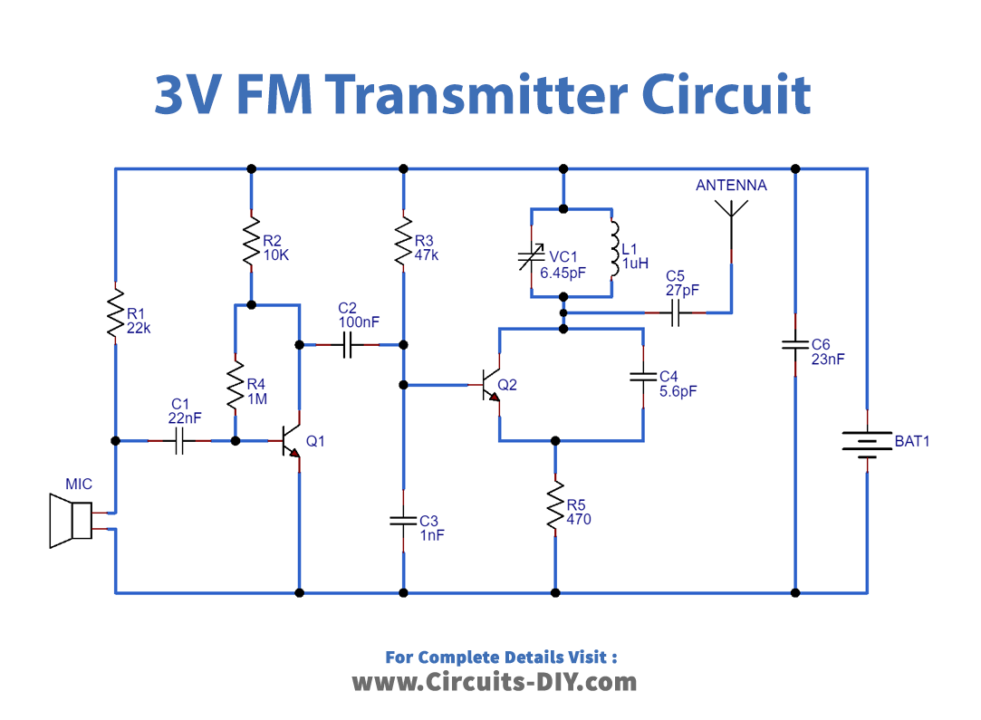
Circuit Operation
In the circuit operation of two transistor FM transmitter circuits, we are discussing the working of this circuit and how this circuit works. The circuit is fundamentally a radio frequency (RF) oscillator that works around 100 MHz. In this transmitter circuit, Sound picked up and enhanced by the electret microphone is fed into the sound amplifier stage which is worked around the main transistor. The yield from the collector is fed into the base of the second transistor where it balances the resonant frequency of the tank circuit (the 5-turn loop and the trim cap) by shifting the junction capacitance of the transistor. Junction capacitance is a component of the potential difference applied to the base of the transistor.
Applications and Uses
These types of FM transmitters are used as
- To communicate a fixed sound source, similar to a PC or a TV, around the home.
- Workaround for playing portable audio devices on car radios that don’t have an Auxiliary “AUX” input jack or Bluetooth sound connectivity.